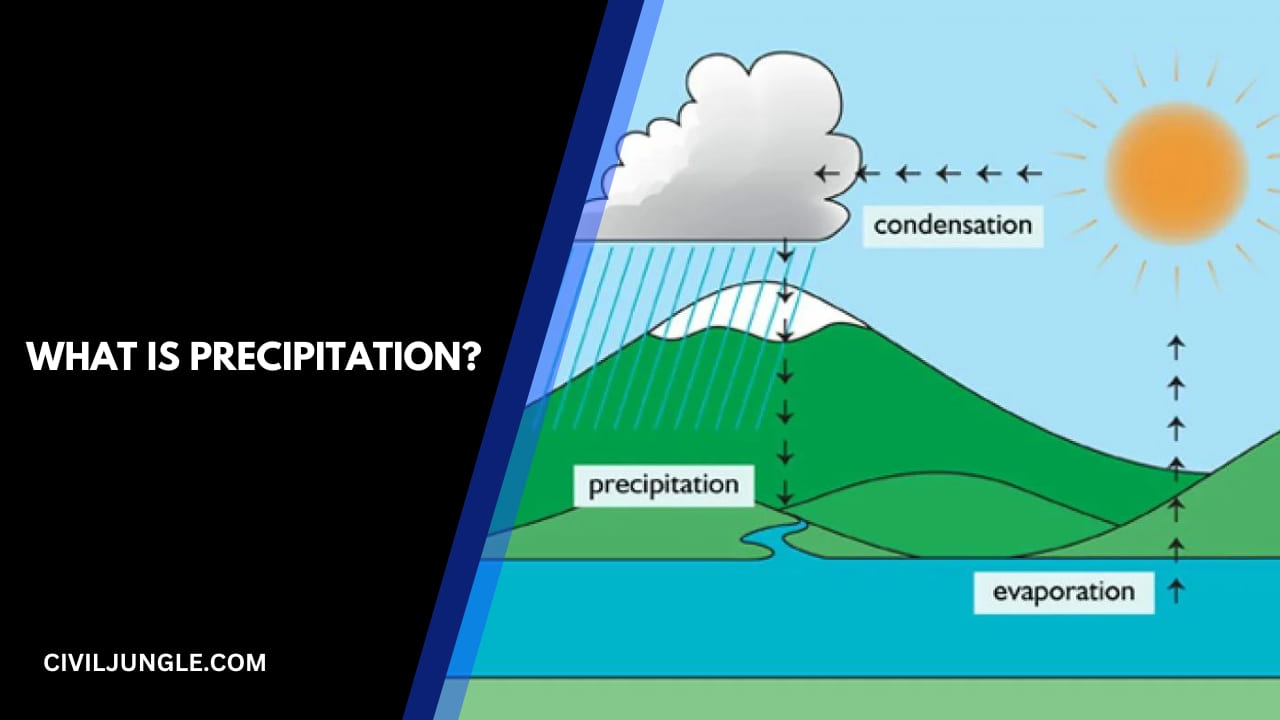
What is Precipitation?
Important Point
Precipitation may be defined as the fall of moisture from the atmosphere to the earth’s surface in any form.
Precipitation
- Liquid Precipitation
- i.e., Rainfall
- Frozen Precipitation
- i.e., Snow
- Hail
- Sleet
- Freezing rain
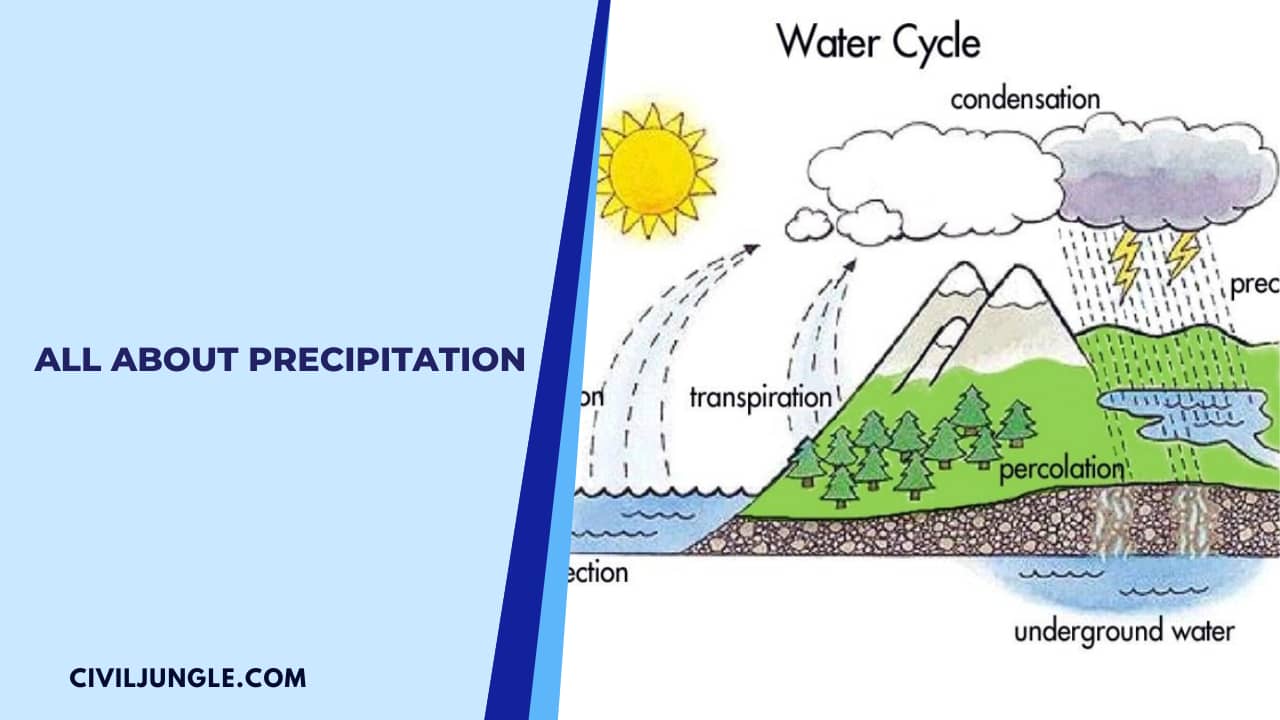
Water evaporates from water surfaces like streams, rivers, oceans, lakes, ponds, etc. And also from land and plants in the form of water vapor.
These water vapors get collected in the atmosphere and behave like a gas.
Under a normal range of temperature and pressure, the water vapor obey the various gas laws (like Boyle’s law, Charles law,etc.). As the evaporation continues, the amount of atmospheric vapor goes on increasing.
But, since space can hold only a certain fixed amount of water vapor in the presence of a solid or a liquid surface, a stage is reached when any further addition of vapor will get condensed on the surfaces.
The vapor may get condensed in different forms, such as mist, rain, snow, hail, sleet, etc. The evaporated water thus returns to the Earth’s surface in any of these forms.
The water which comes back to the surface of the earth in its various forms like rain, hail, snow, sleet, etc. is known as precipitation. In India, a major portion of precipitation is due to rainfall and a small portion of snowfall in the Himalayan region.
For precipitation to form, it therefore necessary to have the following favorable conditions in the environment :
- The atmosphere must have moisture.
- There must be sufficient nuclei (particles) present to aid condensation over them.
- Weather conditions must be favorable to condensation of water vapor.
- The products of condensation must reach to the earth.
Also, read: Trapezoidal Footing Formula with Calculation
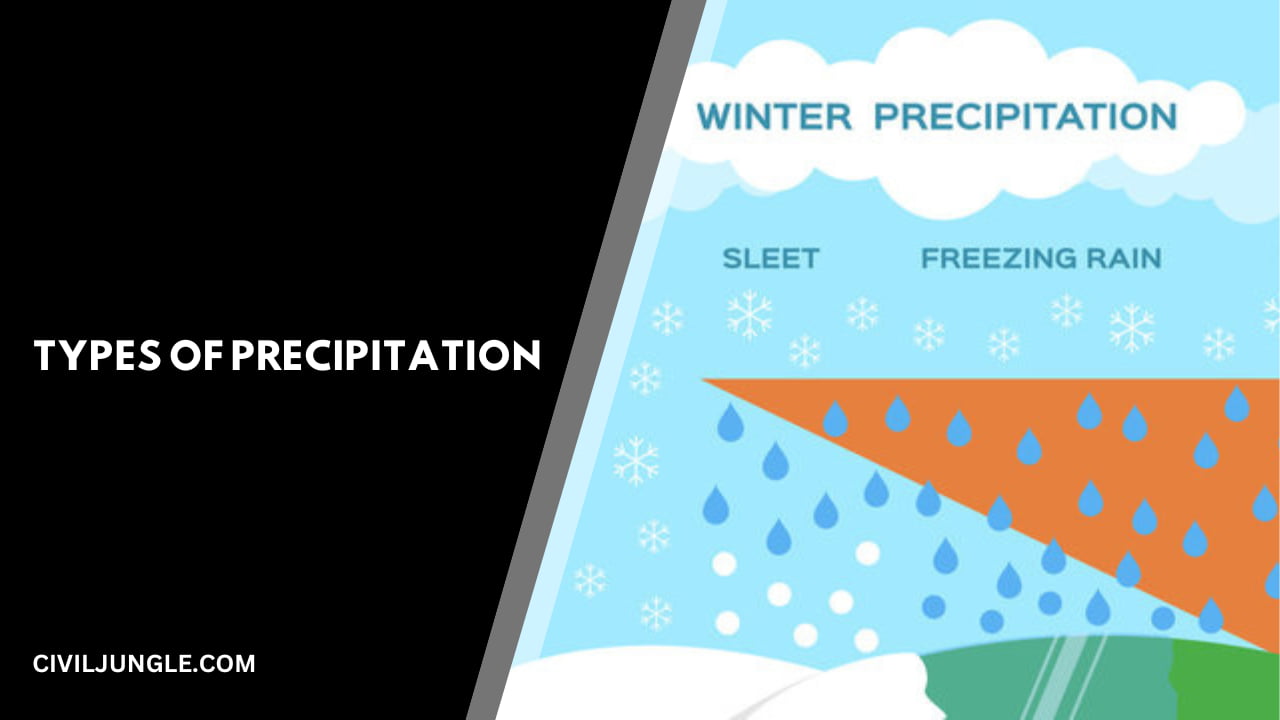
Types of Precipitation
- Cyclonic Precipitation.
- Convective Precipitation.
- Orographic Precipitation.
Precipitation due to turbulent ascent
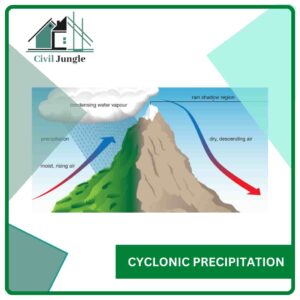
1. Cyclonic Precipitation
Cyclonic precipitation is caused by the lifting of an air mass because of the pressure difference.
If low pressure occurs at an area, air will flow horizontally from the surrounding area, causing the air at the low-pressure area to lift.
The cyclonic precipitation may be divided into two-part
- Frontal Precipitation
- Non-Frontal Precipitation
1.1. Frontal Precipitation:
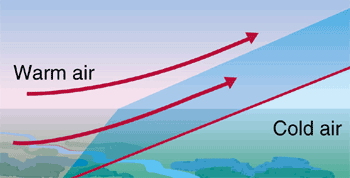
When two air masses, because of contrasting densities and temperatures, clash with each other, precipitation and condensation, occur in the surface of contact.
The surface of contact is called a ‘Front‘ or ‘Frontal Surface,’ and the precipitation is called frontal precipitation.
Cold Front
Warm Front
Stationary Front
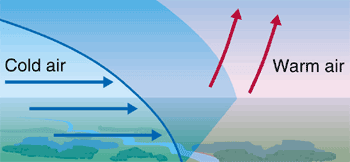
When a cold air mass drives out a warm air mass, it is called a ‘Cold Front,’ and if a warm air mass replaces the retreating cold air mass, it is called a ‘Warm Front.’
On the other hand, if both air masses are drawn simultaneously towards a low-pressure area, the front developed is stationary and is called a ‘Stationary Front.’
Cold Front causes intense precipitation in comparatively small areas, while the precipitation due to the warm front is less intense but is spread over a comparatively larger area. Cold fronts move faster than warm fronts.
Also, read: What is Rate Analysis | Rate Analysis of Earth Work, Brick, Concrete and Plaster
1.2. Non-Frontal Precipitation:
In the case of non-frontal precipitation, the moist warm air mass is stationary, and the moving cold air mass meets it.
Thus, due to the lightness of the warm air mass, there is a passive ascent of warm air over cold air owing to this active undercutting.
When this lifted warm air cools down at higher altitude, precipitation occurs.
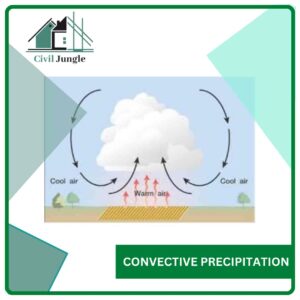
2. Convective Precipitation
Convective Precipitation is caused by the natural rising of warmer lighter air at colder, denser surroundings.
The difference in temperature can result from unequal heating in the surface, unequal cooling in the top of the air layer.
Generally, kind of precipitation occurs in tropics, where, on a hot day, the ground surface gets heated unequally, causing this warmer air to lift up, as the colder air comes to take its place.
The vertical air currents develop tremendous velocities and are hazardous to aircraft. Convective precipitation is spotty, and its intensity vary from light showers to cloud bursts.
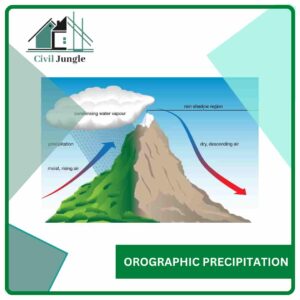
3. Orographic Precipitation
Orographic precipitation is caused by moist air masses. Which strikes some natural topographic barriers like mountains, causing, rise up, condensation, and precipitation.
This greatest amount of precipitation falls on the windward side, and the leeward side often has very little precipitation.
The rainfall is composed of showers and steady rainfall. The winds, heavily laiden with moisture from the Bay of Bengal, strike the southern slope of Himalayas, causing intense rains so much so that a place known as Mawsynram near Cherrapunji in Meghalaya, gets the maximum average annual rainfall of the order of 1270 cm. Similarly, Agumbe In the Western Ghats of South India gets a very heavy orographic rainfall of 900 cm.
Also, read: What Is Passometer & Pedometer | Advantage of Passometer & Pedometer
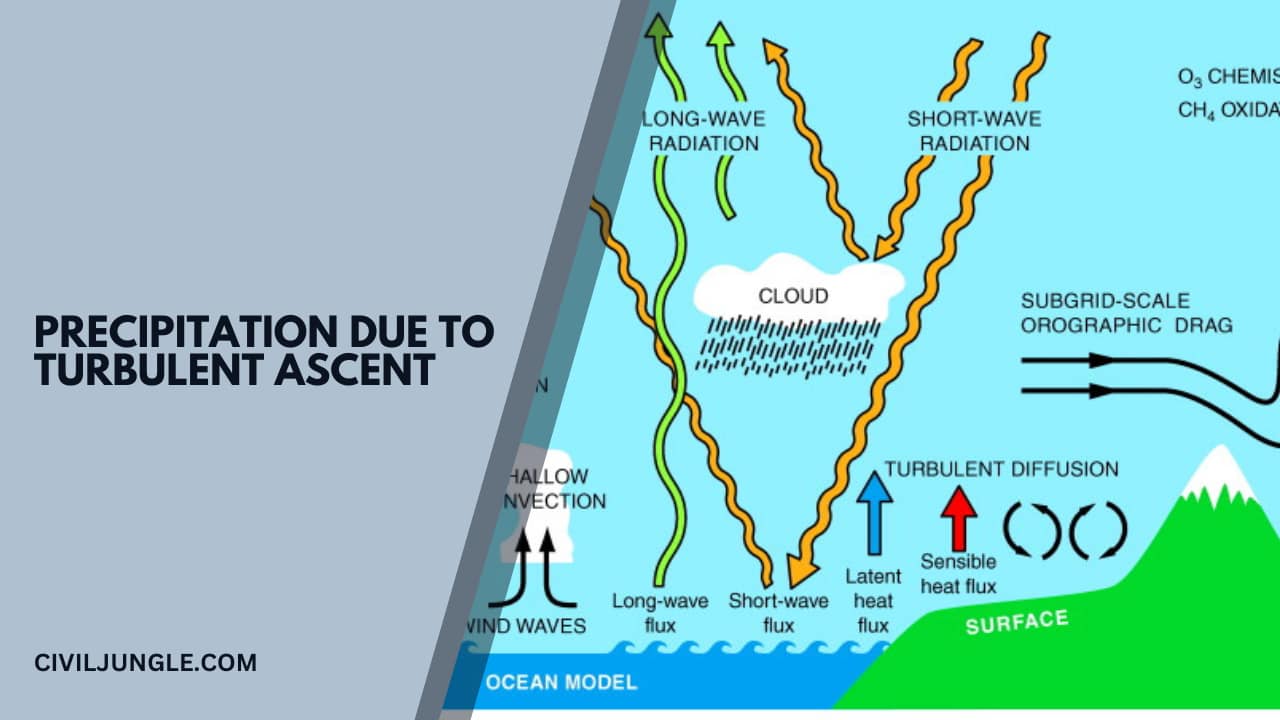
Precipitation Due to Turbulent Ascent
- Air mass is forced to rise up due to greater friction of the earth’s surface after its travel over the ocean.
- The air mass rises up because of increased turbulence and friction when it ultimately condenses, and precipitation occurs.
- Winter rainfall in Madras state is mainly due to this process.
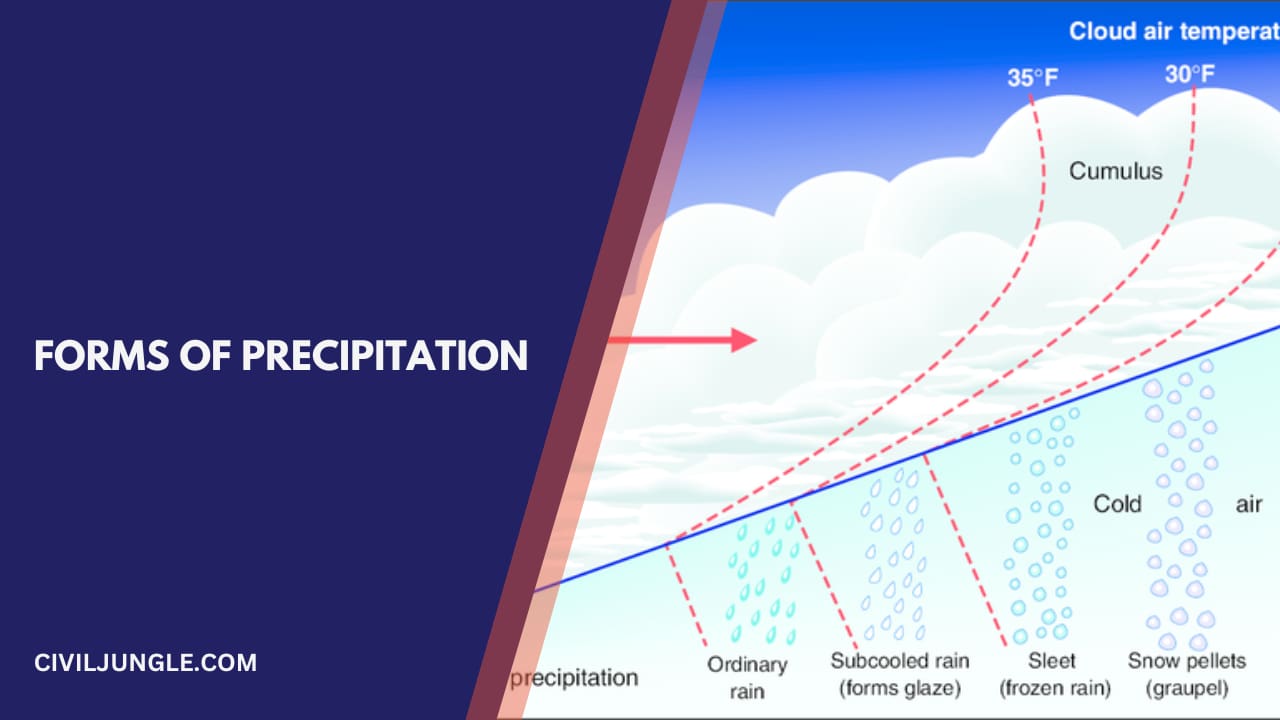
Forms of Precipitation
Different forms of precipitation are as follows.
1. Rain
Rain is the principal form of precipitation in India. When the size of the water drop is larger than 0.5 mm, it is called rainfall. The maximum size of a raindrop is about 6 mm. Any drop larger than this size tends to break down into drops of smaller sizes during its fall from the clouds. On the basis of its intensity, rainfall may be classified as light, moderate, and heavy.
2. Snow
Snow is the next important form of precipitation and consists of ice crystals, usually combining to form flakes. New fresh snow has an initial density of 0.06 to 0.15 g/cu.m. and the average value.’ It is assumed to be 0.10 g/cu.m. Snowfall in India is usually confined only to the Himalayan region. But, in countries like Canada, the USA. Russia. China, etc. where snow occurs in abundance and, hence, forms the major part of their precipitation.
3. Hail
It is showery precipitation in the form of irregular pellets of ice of size more than 8 mm. Hails occur at violent thunderstorms in which vertical currents are very strong
4. Drizzle
A fine sprinkle of numerous water droplets of size, not more than 0.5 mm and Intensity less than 1 nim/h is known as a drizzle. At this, the drops are so small that they appear to float in the air
Also. read: Mortar Vs Grout | What Is Motor and Grout | Type of Motor and Grout | Difference Between Mortar and Grout
5. Sleet
It is frozen raindrops of transparent grains which form if rain falls through the air at subfreezing temperature.
6. Glaze
When rain or drizzle comes at contact with the cold ground at around 0°C. This water drops freeze into form an ice coating called glaze or freezing rain.
7. Rime
It is the white opaque deposit of ice granules more or less separated by trapped air and formed by the rapid freezing of supercooled water drops impinging on exposed objects: Specific gravity can be as low as 0.2 to 0.3.
8. Dew
Dew forms directly by condensation on the ground mainly during the night when the surface has been cooled by outgoing radiation.
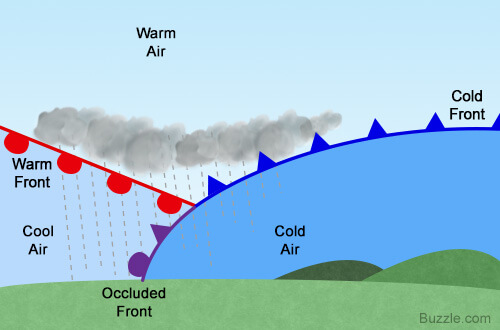
Frontal Precipitation
Frontal precipitation is the result of lifting of lighter warm moist air over more dense cold air. Convective precipitation results from the lifting or upward movement of air that is warmer and lighter than its colder denser surroundings.
What Is Frontal Precipitation?
Frontal precipitation is the result of frontal systems surrounding extratropical cyclones or lows, which form when warm and tropical air meets cooler air. Frontal precipitation typically falls out of nimbostratus clouds.
Cyclonic Rainfall
Cyclonic rainfall, also known as frontal rain, is caused when two air masses of different temperatures meet. Warm air and cool air don´t mix, as they have different densities. As the warm air rises over the heavier cool air, it cools and creates a front; clouds form and produce rain.
How Does Cyclonic Rainfall Occur?
Cyclonic rainfall, also known as frontal rain, is caused when two air masses of different temperatures meet. Warm air and cool air don´t mix, as they have different densities. As the warm air rises over the heavier cool air, it cools and creates a front; clouds form and produce rain.
What Is Frontal and Non Frontal Precipitation?
The precipitation that results is called non–frontal cyclonic precipitation. If one air mass passes over another air mass, the precipitation is frontal cyclonic precipitation. Precipitation caused by cold front is intense and of short duration. Precipitation caused by warm front is more continuous.
How Is Precipitation Important to Weather?
An average raindrop has a mass equivalent to about one million cloud droplets. Because of their large size, precipitation particles have significant falling speeds and are able to survive the fall from the cloud to the ground. In natural clouds, ice crystals form at temperatures colder than about −15 °C (+5 °F).
Where Does Cyclonic Rainfall Occur?
Frontal (or Cyclonic) Rain is caused by cyclonic activity and it occurs along the fronts of the cyclone. It is formed when two masses of air of different temperature, humidity and density meets. For example meeting of moisture laden warm tropical wind with a polar air mass.
Where Does Frontal Precipitation Occur?
Frontal rainfall occurs when a warm front meets a cold front. The heavier cold air sinks to the ground and the warm air rises above it. When the warm air rises, it cools. The cooler air condenses and form clouds.
What Is Precipitation in Hydrology?
Precipitation is the general term for all forms of moisture originating from clouds and falling to the ground. It is that portion of the hydrologic cycle in which atmospheric water vapor is condensed, forming water droplets sufficiently large that gravity causes them to fall to earth.
At What Precipitation Does It Rain?
- When the intensity of the rain trace to 2.5 mm/hr. then is called the Light Rain.
- The intensity is between 2.5 mm/hr. to 7.5 mm/hr for Moderate Rain.
- And if the intensity is greater than 7.5 mm/hr. then it is called the Heavy Rain.
What Is Precipitation in Simple Words?
Precipitation is any liquid or frozen water that forms in the atmosphere and falls back to the Earth. It comes in many forms, like rain, sleet, and snow. Precipitation forms in the clouds when water vapor condenses into bigger and bigger droplets of water. When the drops are heavy enough, they fall to the Earth.
Why Is Cyclonic Rainfall Known as Frontal Rainfall?
Frontal Rainfall is caused by cyclonic activity and occurs along the fronts of a cyclone. when two masses of air of different temperatures meet, they do not mix easily due to temperature and density variations. Fronts are the areas where the rainfall takes place, hence, also called frontal rainfall.
What Are the 3 Types of Precipitation?
The most common types of precipitation are rain, hail, and snow. Rain is precipitation that falls to the surface of the Earth as water droplets.
Why Is Frontal Rainfall Called That?
Frontal rainfall occurs when a warm front meets a cold front. The heavier cold air sinks to the ground and the warm air rises above it. When the warm air rises, it cools. The cooler air condenses and form clouds.
Where Is Frontal Rainfall Most Common?
This rainfall occurs when a warm, tropical air mass comes in contact with a cold, polar air mass. It is very common in Britain and Ireland. Because the air is in the warm front, then it rises over the cold front.
What Are Types of Precipitation?
- Rain: Most commonly observed, drops larger than drizzle (0.02 inch / 0.5 mm or more) are considered rain. However, smaller drops are also considered raindrops if, in contrast to drizzle, they are widely separated.
- Drizzle: Fairly uniform precipitation composed exclusively of fine drops very close together. Drizzle appears to float while following air currents, but unlike fog droplets, it falls to the ground. Quite often fog and drizzle occur together.
- Ice Pellets (Sleet): Precipitation of transparent or translucent pellets of ice, which are round or irregular hard grains of ice consisting of frozen raindrops, or largely melted then refrozen snowflakes.
- Hail: Precipitation in the form of small balls or other pieces of ice falling separately or frozen together in irregular lumps. Associated with thunderstorms, individual hail stones are ¼ inch (5 mm) or greater in diameter. Hail sizes of 1 inch (2.5 cm) or more are indicative of severe thunderstorms.
- Small Hail (Snow Pellets): Precipitation of white, opaque grains of ice that are round or sometimes conical. Diameters are less than ¼ inch (5 mm).
- Snow: Precipitation of snow crystals that are mostly branched and in the form of six-pointed stars.
- Snow Grains: Precipitation of very small, white, and opaque grains of ice. Basically, this is frozen drizzle.
- Ice Crystals: Generally occurring in very cold regions, they are falling crystals of ice in the form of needles, columns, or plates. Also called ‘diamond dust’, ice crystals appear like fog with individual water particles forming directly as ice. The shape of the individual ice crystals causes the ‘light pillar’ optical effect above the light source.
Where Is Frontal Rainfall Experienced?
This rainfall occurs when a warm, tropical air mass comes in contact with a cold, polar air mass. It is very common in Britain and Ireland. Because the air is in the warm front, then it rises over the cold front.
What Causes Frontal Precipitation?
Frontal precipitation is the result of frontal systems surrounding extratropical cyclones or lows, which form when warm and tropical air meets cooler air. When masses of air with different densities (moisture and temperature characteristics) meet, the less dense warmer air overrides the more dense colder air.
What Is a Frontal Rainfall?
Frontal rainfall occurs when a warm front meets a cold front. The heavier cold air sinks to the ground and the warm air rises above it. When the warm air rises, it cools. The cooler air condenses and form clouds. The clouds bring heavy rain.
What Triggers Precipitation?
Precipitation forms in the clouds when water vapor condenses into bigger and bigger droplets of water. When the drops are heavy enough, they fall to the Earth. If a cloud is colder, like it would be at higher altitudes, the water droplets may freeze to form ice.
Why Frontal Rainfall Is Called So?
In this type of rainfall warm moist air encounters colder more dense air at regions we call fronts. Because the warm air is less dense since it has more energy it is forced to rise above the colder denser air.
What Does Frontal Rainfall Mean?
Frontal rainfall occurs when a warm front meets a cold front. The heavier cold air sinks to the ground and the warm air rises above it. When the warm air rises, it cools. The cooler air condenses and form clouds.
What Are the Characteristics of Frontal Rainfall?
Frontal rainfall occurs when a warm front meets a cold front. The heavier cold air sinks to the ground and the warm air rises above it. When the warm air rises, it cools. The cooler air condenses and form clouds.
What Does Precipitation Mean?
The phenomenon of condensation of water vapor, forming the product in the form of Rainfall, Snowfall, Dew, and frost falls on the earth’ssurface under the action of gravitational force is Known as Precipitation.
What Is Precipitation and Examples?
Precipitation includes rain, hail, sleet, and snow. Snow is ice that falls from the sky. Snow forms when water vapor turns directly from a gas into its solid form, ice, in a process called deposition.
How Does Precipitation Contribute to Weather?
Global Climate Change. comes from precipitation. Too little precipitation can result in dry soil, shallow streams, and shortages of municipal water supplies. For example, too much rain or snowmelt (water from melted snow) at one time can lead to flooding.
What Is the Importance of Precipitation?
Precipitation is important because it helps maintain the atmospheric balance. Without precipitation, all of the land on the planet would be desert. Precipitation helps farmers grow crops and provides a fresh water supply for us to drink. Precipitation can also be damaging.
What Is Precipitation and How Does It Affect Weather?
As temperatures rise and the air becomes warmer, more moisture evaporates from land and water into the atmosphere. More moisture in the air generally means we can expect more rain and snow (called precipitation) and more heavy downpours.
What Does Precipitation Mean in Weather?
When we talk about precipitation, we are talking about water that is falling out of the sky, this could be rain, drizzle, snow, sleet, hail or something rarer!
Is Precipitation Good or Bad?
Rainfall and other precipitation washes nutrients from human activities like agriculture and fossil fuel combustion into rivers and lakes. When these waterways get overloaded with nutrients, a phenomenon called “eutrophication,” the results can be dangerous.
Is fog a form of precipitation?
Precipitation. Precipitation fog forms as precipitation falls into cold, drier air below the cloud and evaporates into water vapor. The water vapor cools and at the dew point it condenses. When it condenses, it creates fog.
Types of Precipitation
Precipitation refers to any form of water that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface. There are several types of precipitation, each characterized by the physical state and size of the water particles. The most common types of precipitation include:
- Rain: Rain is the most familiar form of precipitation. It occurs when liquid water droplets in the atmosphere combine and fall to the ground. Raindrops have a diameter of at least 0.5 millimeters.
- Snow: Snow occurs when water vapor in the atmosphere freezes into ice crystals without melting into liquid first. These ice crystals then combine to form snowflakes. Snowflakes can vary in size and shape, and they fall to the ground as individual flakes.
- Sleet: Sleet consists of small ice pellets or frozen raindrops. It forms when raindrops fall through a layer of freezing air near the Earth’s surface, causing them to freeze before reaching the ground. Sleet can bounce when it hits a surface.
- Freezing rain: Freezing rain is similar to sleet but differs in that raindrops do not freeze completely. Instead, they become supercooled upon contact with a cold surface, forming a layer of ice. Freezing rain can create hazardous conditions, as it can coat surfaces such as roads and power lines with ice.
Precipitation Measurement Methods
Liquid precipitation is traditionally measured using various types of rain gages such as the non-recording cylindrical container type or the recording weighing type, float type and tipping-bucket type. All of the above gages measure precipitation at a point.
Effects of Precipitation on Agriculture
Soil is also greatly affected by rainfall. If it is too wet or too dry, nutrients in the soil can run off and not make it to the plants’ roots, leading to poor growth and overall health. Additionally, as mentioned previously, overwatering or too much rain can also lead to bacteria, fungus, and mold growth in the soil.
Precipitation Vs. Evaporation
Precipitation is comprised of rain and snow that falls to Earth’s surface from the clouds. Evaporation is the change in phase of liquid water from the Earth’s surface to water vapor in the atmosphere. Arguably, precipitation and evaporation are the two most important components of the water cycle!
Preventing Precipitation Damage to Roofs
8 tips to protect your roof from storm damage
- Roof inspection. A regular roof inspection is important to detect possible damage. …
- Repair or replace roof.
- Cut down the trees or large bushes.
- Clean your gutters.
- Remove any outside objects.
- Install a durable roofing material
- Hire a roofing contractor.
- Ventilate your roof properly.
What Is Cyclonic Rainfall?
Cyclonic rainfall refers to a type of rainfall that occurs in association with cyclones, also known as tropical storms or hurricanes. Cyclones are large-scale weather systems characterized by low-pressure centers with circulating winds. These storms form over warm ocean waters and are typically accompanied by heavy rainfall, strong winds, and thunderstorms.
What Is Frontal Rainfall?
This is when cold air meets warm air in a ‘weather front’. Warm air rises, so when it bumps into the cold air, it rises above it. However, like when you’re climbing a hill, the higher you go up in the atmosphere, the colder it is.
What Is Precipitation?
Precipitation refers to any form of water, in liquid or solid state, that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface. It is a vital part of the Earth’s water cycle and plays a crucial role in sustaining life and shaping the environment.
What Is Cyclonic Precipitation?
Cyclonic precipitation refers to the type of rainfall or precipitation that occurs in association with cyclones or low-pressure systems. Cyclones are large-scale weather systems characterized by the rotation of air around a central low-pressure area. They are also commonly known as hurricanes or typhoons, depending on the region in which they occur.
What Type of Precipitation Occurs When Air Masses Rise Over Mountains Causing It to Condense and Rain?
orographic precipitation, rain, snow, or other precipitation produced when moist air is lifted as it moves over a mountain range. As the air rises and cools, orographic clouds form and serve as the source of the precipitation, most of which falls upwind of the mountain ridge.
What Is Precipitation in Weather?
Precipitation is any liquid or frozen water that forms in the atmosphere and falls back to the earth. It comes in many forms, like rain, sleet, and snow. Along with evaporation and condensation, precipitation is one of the three major parts of the global water cycle.
Frontal Precipitation
Frontal precipitation is the result of frontal systems surrounding extratropical cyclones or lows, which form when warm and tropical air meets cooler, subpolar air. Frontal precipitation typically falls out from nimbostratus clouds.
Convective Precipitation
Convective precipitation occurs when warm, moist air rises in the atmosphere. Pressure decreases as elevation increases, which causes the temperature to fall. If the moist air mass rises to a sufficiently high elevation, precipitation will condense and fall.
Suggested Read –
- Para Pit
- Top 15+ Best Plywood Brands in India
- 20 Types of Plumbing Pipes for Different Use
- What is BoQ | BoQ Meaning | Advantages of BoQ | What is BoM
- What Is Lap Length | Lap Length of Column | Lap Length of Slab | Lap Length of Beam
- Detail of Beam Connection | Simple Framing Connection | Semi-Rigid Framing Connection | Rigid Frame Connection
- What Is Bond Breaker | Purpose of Providing Bond Breaker | What Is Concrete Bond Breaker | What is Bond Breaker Tape
- What Is Hard Hat | Hard Hat Colour Definition | Different Hard Hat Colour Codes | Types of Safety Helmets | Classification of Hard Hats
Originally posted 2023-07-08 12:55:32.









Usually I do not read post on blogs, however I would like to say that your blog is very pressured to read! Your writing style has been amazed me. Thanks, very nice post.
Thanks for the article post.Really thank you! Great.