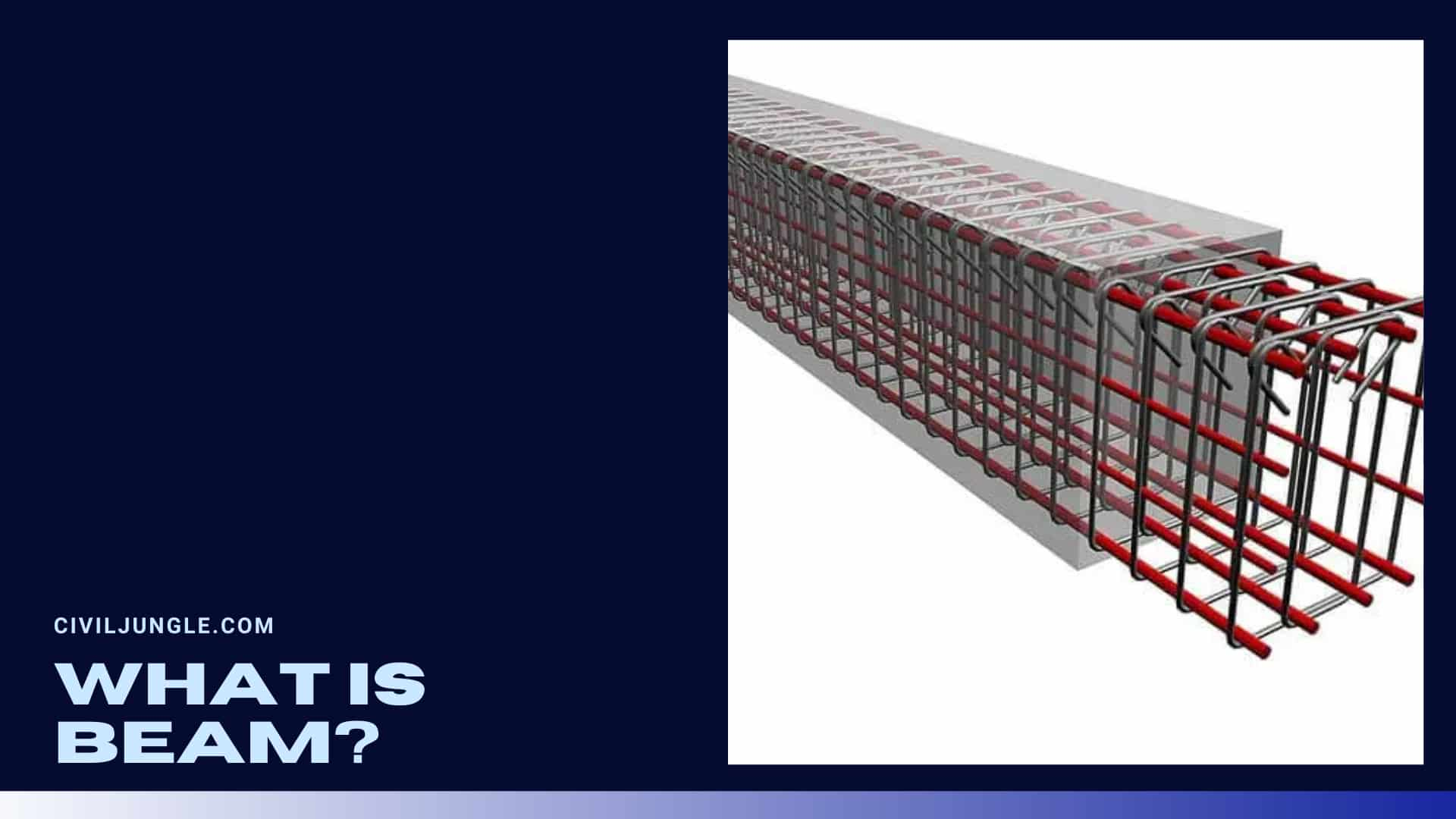
What Is Beam?
Important Point
The beam is a structural element that stands against the bending. Mainly beam carries vertical gravitational forces, but also pull the horizontal loads on it.
The beam is called a wall plate or sill plate that carries the transmits and load it to the girders, columns, or walls. It is attached with.
In the early centuries, timbers were the most preferred material to be used as a beam for this structural support purpose, now to bear the force along with carrying vertical gravitational force, now they are made up of aluminum, steel, or other such materials.
In actual means, beams are these structural materials, which bear the sheer force of the load and the bending moment.
To carry on the more tension and load, pre-stressed concrete beams are widely used nowadays in the foundation of bridges and other such humongous structures.
Several famous beams used nowadays are supported Beam, Fixed Beam, Cantilever Beam, Continuous Beam, Overhanging Beam.
Also, read: What is Plum Concrete | Application | Mix Design | Methodology
Construction Beams
In building construction, a beam is a horizontal member spanning an opening and carrying a load that may be a brick or stone wall above the opening, in which case the beam is often called a lintel (see post-and-lintel system).
Types of Beam
5 Different types of beam are as follows.
- Simply Supported Beam.
- Cantilever Beam.
- Over Hanging Beam.
- Continuous Beam.
- Fixed Ended Beam.
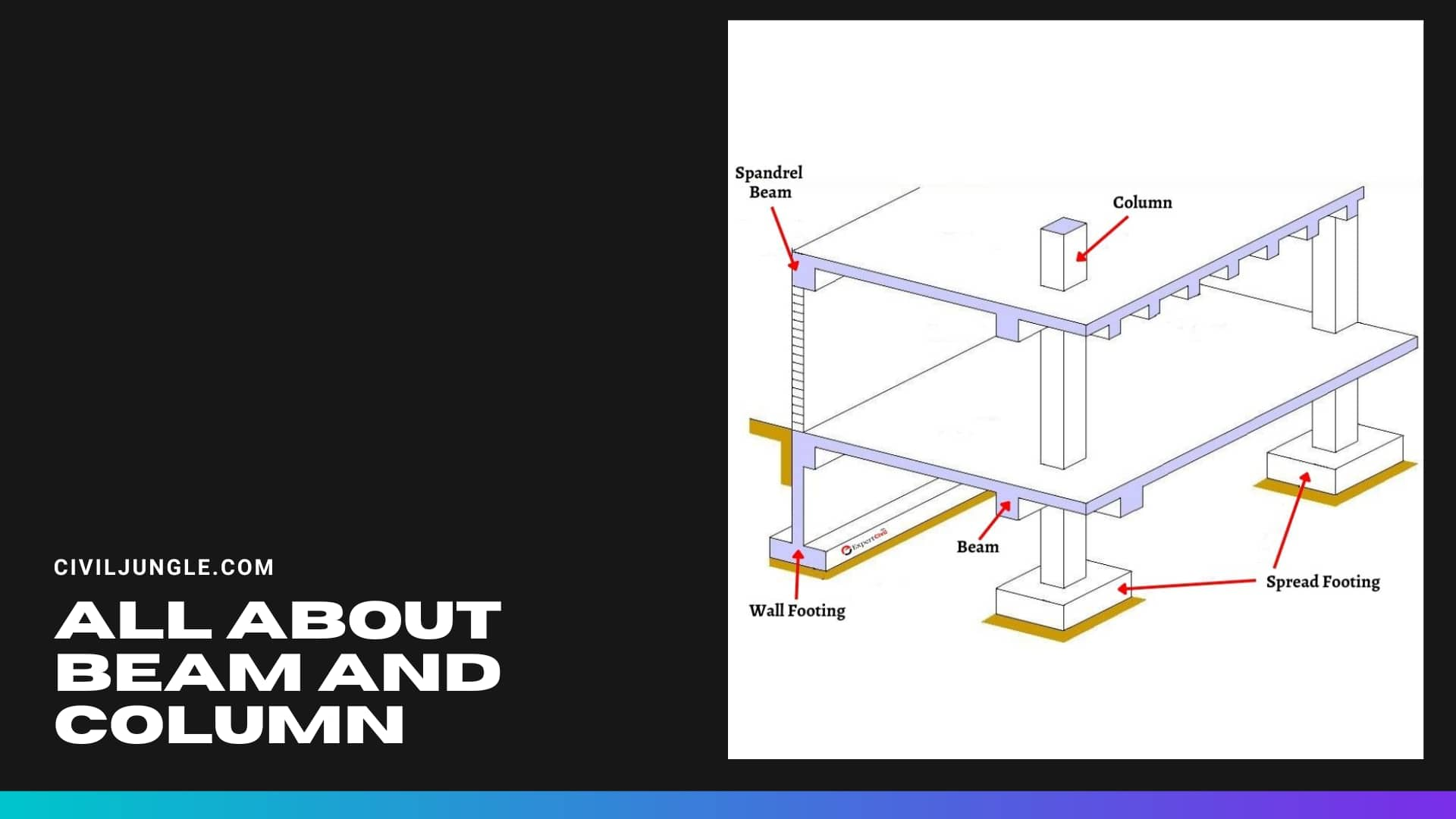
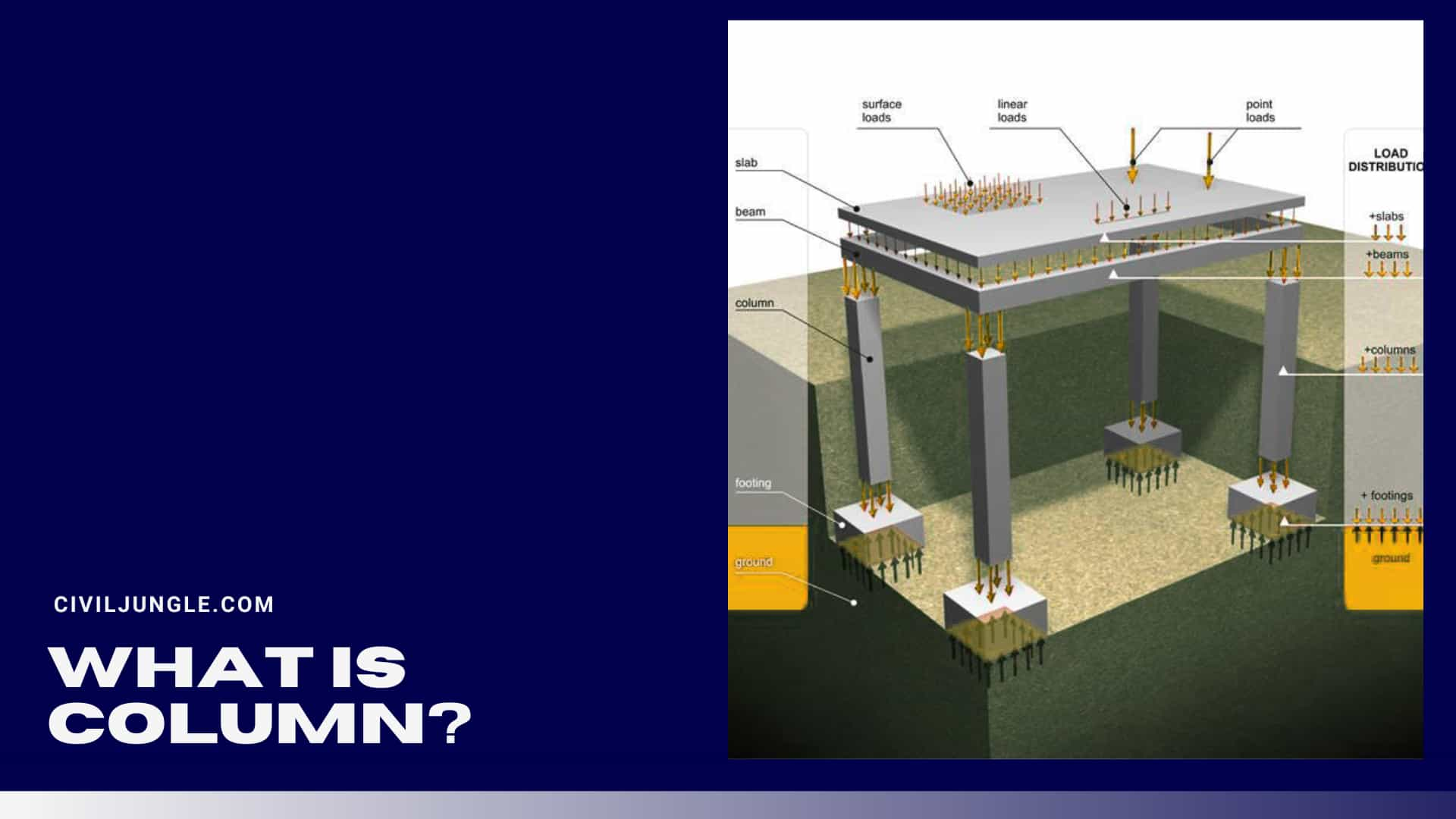
What Is Column?
A compression member, i.e., column, is an important element of every reinforced concrete structure. These are used to transfer a load of superstructure to the foundation safely.
Mainly columns, struts, and pedestals are used as compression members in buildings, bridges, supporting systems of tanks, factories, and many more such structures.
A column is defined as a vertical compression member who is mainly subjected to the effective length and axial loads of which exceeds three times its least lateral dimension.
The compression member whose effective length is less than three times its least lateral dimension is called Pedestal
Shape of Column
The compression member who is inclined or horizontal and is subjected to axial loads is called Strut. Struts are used in trusses.
The function of columns is to transfer the load of the structure vertically downwards to transfer it to a foundation.
Apart from the wall performs the following functions also:
- It encloses building areas into different compartments and provides privacy.
- It provides safety from burglary and insects.
- It keeps the building warm in cools in summer and winter.
Also, read: What Is Honeycomb In Concrete | Cause | Cure | Type of Grouting
Types of Column
15 Different types of Column are as follows.
- Tied Column
- Spiral Column
- Composite column
- Axially Loaded Column
- Column with Uniaxial Eccentric Loading
- Column with Biaxial Eccentric Loading
- Short Column
- Long Column
- Square or Rectangular Column
- Circular column
- L-Shape Column
- T-Shape column
- Shape of Steel Column
- Shape of Composite Column
- Reinforced Concrete, Steel, timber, Brick, Block, and Stone Column.
Also, read: What Is Spalling Concrete | Causes of Spalling in Concrete | Repairing Concrete Spalding
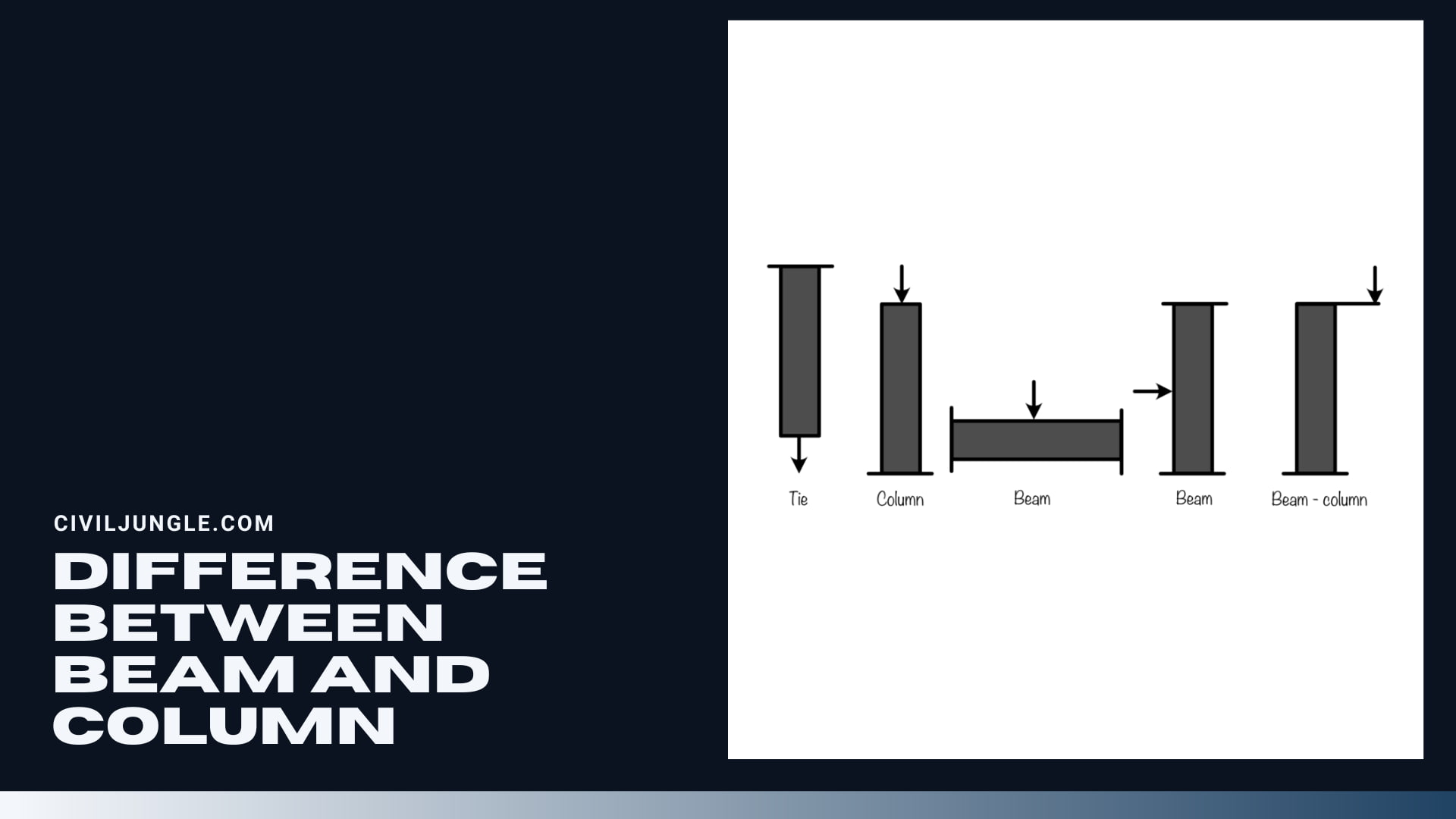
Difference Between Beam and Column
The minimum width of the beam is 200 mm. The minimum width of a column is 200 mm, however, for earthquake resistance, it should be 300mm.
| Sr.No. | Beam | Column |
| 1 | Communally a horizontal member of a structure that resists transverse load is called a beam. | Communally a vertical member of a structure that resists axial/eccentric load is called a column. |
| 2 | The beam is carried load perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. | The column is carried load parallel to the longitudinal axis. |
| 3 | Beam is basically carried or resists bending and shear force. | Column is basically carried or resists compression load. |
| 4 | Beams shapes can be square, rectangular, T shape, I shape, H shape. | Column shape can be rectangular, circular, square, T shape, L shape, C shape, elliptical etc |
| 5 | Minimum width of the beam is 200 mm. | Minimum width of a column is 200 mm, however, for earthquake resistance, it should be 300mm. |
| 6 | Longitudinal steel in Beam is on two faces which are used to resist bending moment while the vertical loads are resisted by stirrups or inclined beam | Longitudinal steel in Column is on all faces which basically resists compression |
| 7 | Communally cast with slab and hence greater care is observed for its concreting and curing in case of RCC structures. | Communally cast in small batches and hence the quality of concreting as well as curing ignored in case of RCC structures. |
| 8 | Beam without building possible | Here, Column important part of building |
Beams and Columns
When discussing the beam and column difference, it’s essential to understand that beams and columns are two important types of beams and columns in structural elements that play a key role in creating a safe load path to transfer the weight and forces on a structure to the foundations and into the ground. Beams are usually horizontal structural elements that carry loads perpendicular to their longitudinal direction.
What Are Beams?
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally to the beam’s axis. Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending. The loads applied to the beam result in reaction forces at the beam’s support points.
How Are Beams Different from Columns?
Considering the difference between column and beam, a column is the vertical structural element which is attached to roof slab, beam or ceiling, and it transfers load to the footings of building, whereas Beam is a structural element to carry the loads from the slabs to the columns and with stand against the bending.
How Beams and Columns Are Connected?
The standard way of connecting beams to columns is to provide moment transfer through full penetration butt welds between the beam flanges and column flanges (strong axis connections) or continuity plates (weak axis connections) and to provide shear transfer through the beam web connection.
What Is Column in Structure?
When asking what is beam and column, one should know that a column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural elementthat transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest.
Can a Beam Be Used as a Column?
Beams and columns could be built using the same shapes and materials but each serves a different function and is designed differently. Beams are used to support the weight of floors, ceilings and roofs of a building and to transfer the load to a vertical load bearing element of the structure.
What Is Slab Beam and Column?
Slab is an important structural element which is constructed to create flat and useful surfaces such as floors, roofs, and ceilings. Commonly, slabs are supported by beams, columns (concrete or steel), walls, or the ground. The depth of a concrete slab floor is very small compared to its span.
Are Beams the Same as Columns?
In the context of beams and columns in building construction, a beam is a horizontal structural element which withstands vertical loads whereas columns are basically vertical members which span from substructure to superstructure and play a crucial role in transfer of load from top of structure to bottom footing.
What Is the Difference Between a Beam and Pillar?
In the context of pillar vs column vs beam, in architecture and building construction, pillar refers to any isolated, vertical structural member such as a pier, column, or post. A beam is a structural element that is capable of bearing load principally by resisting against bending.
How Do You Place Columns and Beams?
When designing a building having beams and column is called a structure, columns should preferably be located at (or) near the corners of a building, and at the intersection of beams/walls. Select the position of columns so as to reduce bending moments in beams. Avoid larger spans of beams. Avoid larger centre-to-centre distance between columns.
Buildings Columns
- Tied Column.
- Spiral Column.
- Composite Column.
- Axially Loaded Column.
- Column with Uniaxial Eccentric Loading.
- Column with Biaxial Eccentric Loading.
- Short Column.
What Is Supporting Column?
Supporting Column- a column that supports a heavy weight.
Construction Beams
Construction beams are horizontal, weight-bearing supports that bridge an area. Along with posts and columns, which are the beams’ vertical counterparts, they support the structural integrity of all sorts of buildings. In homes, you’ll find beams in walls, floors, ceilings, roofs, decks, and garages.
Uses of Beams
Beams support the weight of a building’s floors, ceilings, and roofs and to move the load to the framework of a vertical load bearing element. In order to withstand the combined weight of stacked walls and transfer the support load, often larger and heavier beams called transfer beams are used.
Beams Construction
Construction beams are horizontal, weight-bearing supports that bridge an area. Along with posts and columns, which are the beams’ vertical counterparts, they support the structural integrity of all sorts of buildings. In homes, you’ll find beams in walls, floors, ceilings, roofs, decks and garages.
Beam Definition Engineering
A beam, in Structural Engineering terms, is a member that can be comprised of a number of materials (including steel, wood aluminum) to withstand loads – typically applied laterally to the beam axis. Beams can also be referred to as members, elements, rafters, shafts, or purlins.
What Is Beam?
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally to the beam’s axis. Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending. Beams are characterized by their manner of support, profile (shape of cross-section), equilibrium conditions, length, and their material.
Construction Columns
A column is a vertical structural member intended to transfer a compressive load. Columns are typically constructed from materials such as stone, brick, block, concrete, timber, steel, and so on, which have good compressive strength.
What Is a Structural Column?
Structural columns are used to model vertical load-bearing elements in a building. Structural columns differ from architectural columns in behavior as well. Structural elements such as beams, braces, and isolated foundations join to structural columns; they do not join to architectural columns.
Do Columns Support Beams?
Columns are used to support floor/roof beams and the columns of the floor above. The columns at the bottom floor of a tall building must carry the accumulative weight of all the floors above. This is why the location of columns ideally should be consistent throughout all floors.
What Are Columns in Buildings?
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest.
Structural Pillars
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest.
Types of Structural Columns
- Circular columns
- Composite columns
- L-shape columns
- Short reinforced columns
- Spiral reinforced concrete columns
- Square or rectangular columns
- Stub columns
- Tension columns
Building Beam
In building construction, a beam is a horizontal member spanning an opening and carrying a load that may be a brick or stone wall above the opening, in which case the beam is often called a lintel (see post-and-lintel system).
Beam Architecture
In building construction, a beam is a horizontal member spanning an opening and carrying a load that may be a brick or stone wall above the opening, in which case the beam is often called a lintel (see post-and-lintel system).
What Are Columns Made of?
Modern columns tend to be made of iron, steel, or concrete and are simply designed.
What Is a Beam in Engineering?
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally to the beam’s axis. Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending. The loads applied to the beam result in reaction forces at the beam’s support points.
Structural Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest.
Building Support Beams
Construction beams are horizontal, weight-bearing supports that bridge an area. Along with posts and columns, which are the beams’ vertical counterparts, they support the structural integrity of all sorts of buildings. In homes, you’ll find beams in walls, floors, ceilings, roofs, decks and garages.
What Are the Types of Beams in Construction?
In engineering, beams are of several types: Simply supported – a beam supported on the ends which are free to rotate and have no moment resistance.
What Are Large Vertical Structures That Help Support the Weight of the Structure Overhead?
A column is a type of structure that helps transmit the weight of a structure above to the elements located below. In this way, a column helps support the weight of the structure overhead. Columns operate through compression.
What Are I Beams Made of?
I-Beams, also known as H-Beams have and I or H cross-section. I-Beams are commonly made of structural steel but can be formed out of aluminum. I-beams are most widely used in construction and can have an application for use in both beams as well as columns.
What Is a Support Beam?
Construction beams are horizontal, weight-bearing supports that bridge an area. Along with posts and columns, which are the beams’ vertical counterparts, they support the structural integrity of all sorts of buildings.
Why Are I Beams Used?
I beams are the choice shape for structural steel builds because of their high functionality. The shape of I beams makes them excellent for unidirectional bending parallel to the web. The horizontal flanges resist the bending movement, while the web resists the shear stress.
Why Are I Beams Used Instead of Rectangular Beams?
I beams are the choice shape for structural steel builds because of their high functionality. The shape of I beams makes them excellent for unidirectional bending parallel to the web. The horizontal flanges resist the bending movement, while the web resists the shear stress.
What Are I Beams Used for?
I beams have a variety of important uses in the structural steel construction industry. They are often used as critical support trusses, or the main framework, in buildings. Steel I beams ensure a structure’s integrity with relentless strength and support.
Difference Between Column and Pillar
A pillar is a vertical support member and may be constructed as a single piece of timber, concrete or steel, or built up out of bricks, blocks and so on. However, whereas a pillar does not necessarily have a load-bearing function, a column is a vertical structural member that is intended to transfer a compressive load.
What Is the Difference Between a Pillar and a Column?
A pillar is a vertical support member and may be constructed as a single piece of timber, concrete or steel, or built up out of bricks, blocks and so on. However, whereas a pillar does not necessarily have a load-bearing function, a column is a vertical structural member that is intended to transfer a compressive load.
What Does Beam Stand for?
Beam is a framework for discussing the usefulness of different types resources. Developed by Joseph Bizup as a more functional alternative to the traditional primary/secondary classification, BEAM stands for Background, Exhibit, Argument, and Method.
How Are I Beams Made?
There are two standard I-beam forms: Rolled I-beam, formed by hot rolling, cold rolling or extrusion (depending on material). Plate girder, formed by welding (or occasionally bolting or riveting) plates.
Why Is an I Beam So Strong?
I beams are the choice shape for structural steel builds because of their high functionality. The shape of I beams makes them excellent for unidirectional bending parallel to the web. The horizontal flanges resist the bending movement, while the web resists the shear stress.
What Are Beams and Columns?
The beam is a horizontal structural component that mainly carries vertical loads. … In contrast, columns are vertical compression members that span from substructure to superstructure and have a vital role in transferring load from the top of the structure to the foundation.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read-
- Bond Beam Vs Lintel
- Single Reinforced Beam
- Isolated Column Footing
- Difference Between I Beam and H Beam
- Difference Between Lap Length and Development Length
- Difference Between Plasticizer And Superplasticizer in Civil
- Tension Vs Compression | What Is Tension & Compression
- Difference Between Plinth Level, Sill Level, and Lintel Level
- Difference Between One Way Slab and Two Way Slab | What is Slab
- Difference Between Timber And Wood | What is Wood | What is Timber
- Difference Between Bridge and Culvert | What Is Bridge | What Is Culvert
- Difference Between Flyover and Bridge | What Is Flyover | What Is Bridge
- Difference Between M Sand Vs River Sand | What is M-Sand & River Sand
- Difference Between Footing and Foundation | What is Footing and Foundation
- Difference Between OPC Vs PPC | What is Cement | OPC Cement | PPC Cement
- Difference Between Short Column and Long Column | What Is Column | Type of Column
- Difference Between Mortar and Concrete | What Is Mortar & Concrete | Type of Mortar &Concrete
- Difference Between Flexible Pavement and Rigid Pavement | What is Pavement | Type of Pavement
- Difference Between Pre-Tensioning and Post-Tensioning | What Is Prestressed | Methods of Prestress
Originally posted 2023-08-12 14:45:40.


Amazing post, thanks for sharing this knowledgeable post.
Thanks