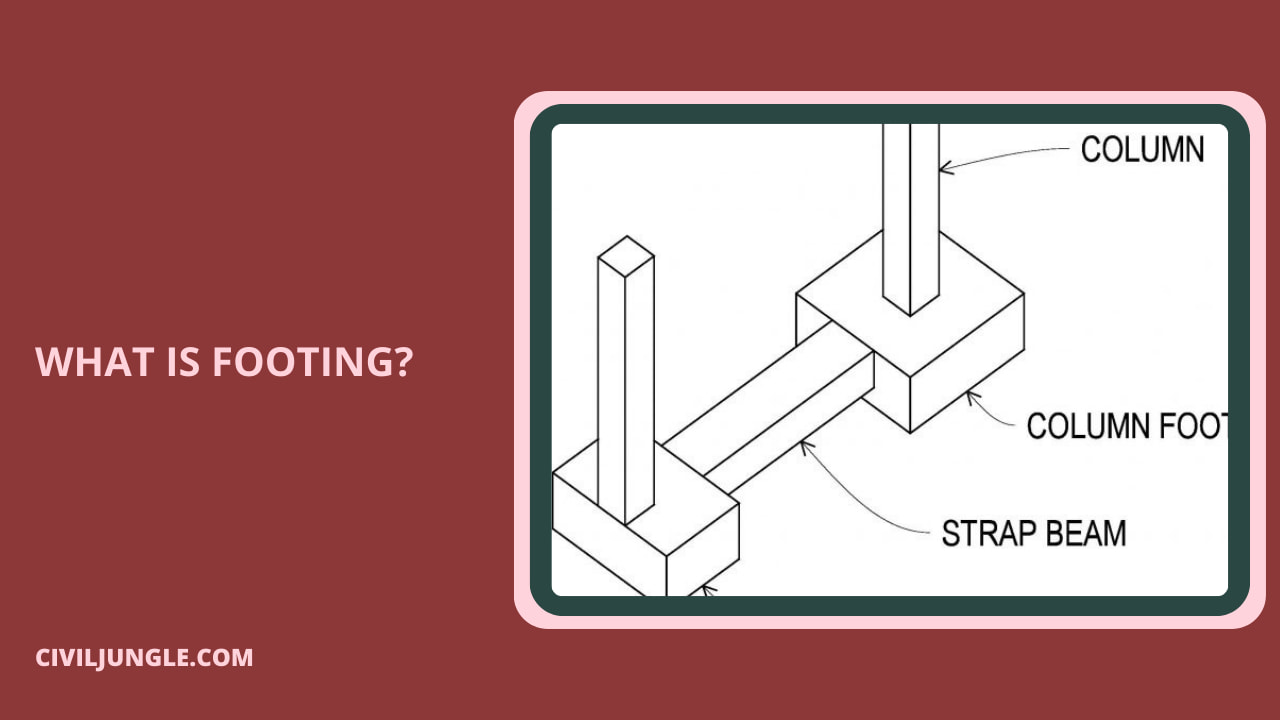
What is Footing?
Important Point
Foundation Definition: The footing foundation is generally supporting columns and may be round, square, or rectangular at a plan and in section.and may be round, square, or rectangular at a plan and in section.
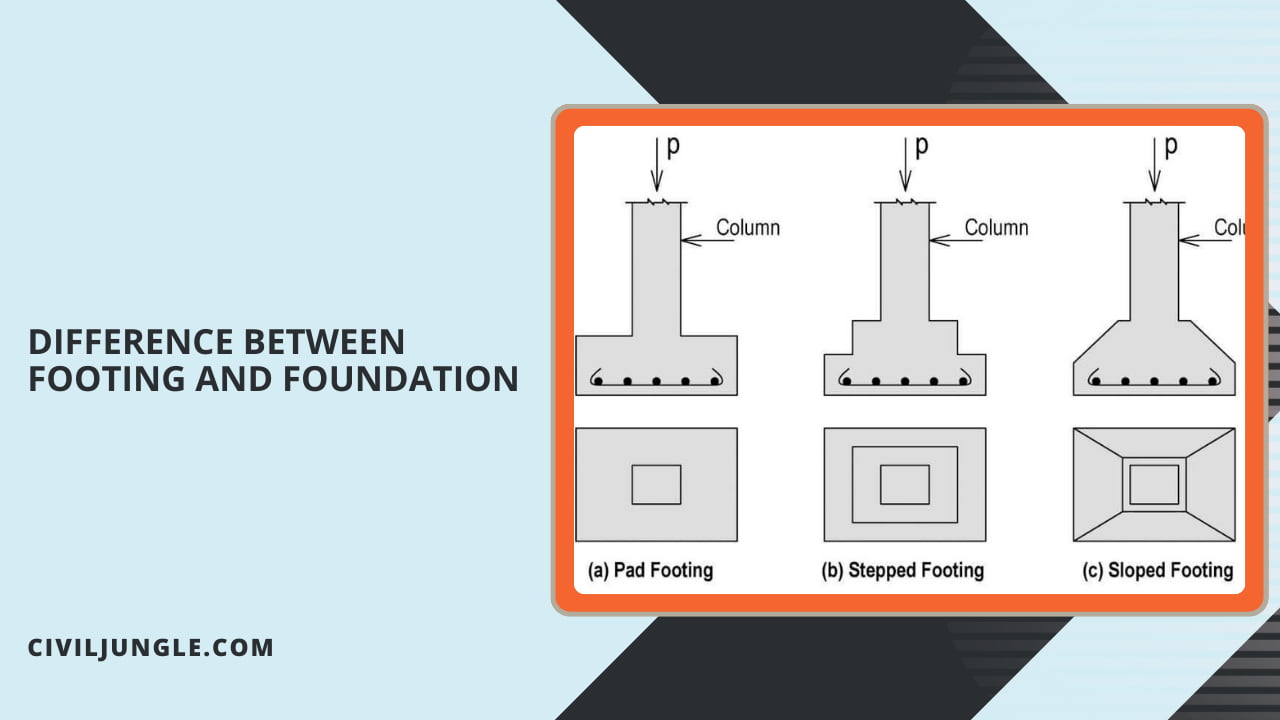
They may be of the slab — stepped or sloping type. Thia stepped footing results at a better distribution of load than a slab footing.
A sloped footing isn’t less economical, although constructional problems are associated with this sloping surface.
The isolated spread footing at plain concrete has the advantage that the column had is transferred to the soil through dispersion at the footing.
Foundation detail: In reinforced concrete footings. i.e., pads. This slab is treated as an inverted cantilever bearing this soil pressure and supported by the column.
Where a two-way footing is provided, it can be reinforced at two directions of bending with bars of steel placed in this bottom of the pad parallel to its sides.
If clearances permit, two-way square footings used to reduce the bending moments. Where not less than one column is placed on pads (combined footing).
Their shapes can be rectangular or trapezoidal; the latter produces a more economical design where large differences of the magnitude of the column loads exist or where rectangular footings cannot be accommodated.
This gives pad-type/ combined footings and their behavior under external loads and bearing pressures: typical reinforcement detailing for two different combined footings in sectional elevations and plan.
The specifications and quantities can change depending on the column loads and the spread area.
Also, read: What Is Raft Foundation | Type of Footing | Detail of Raft Footing
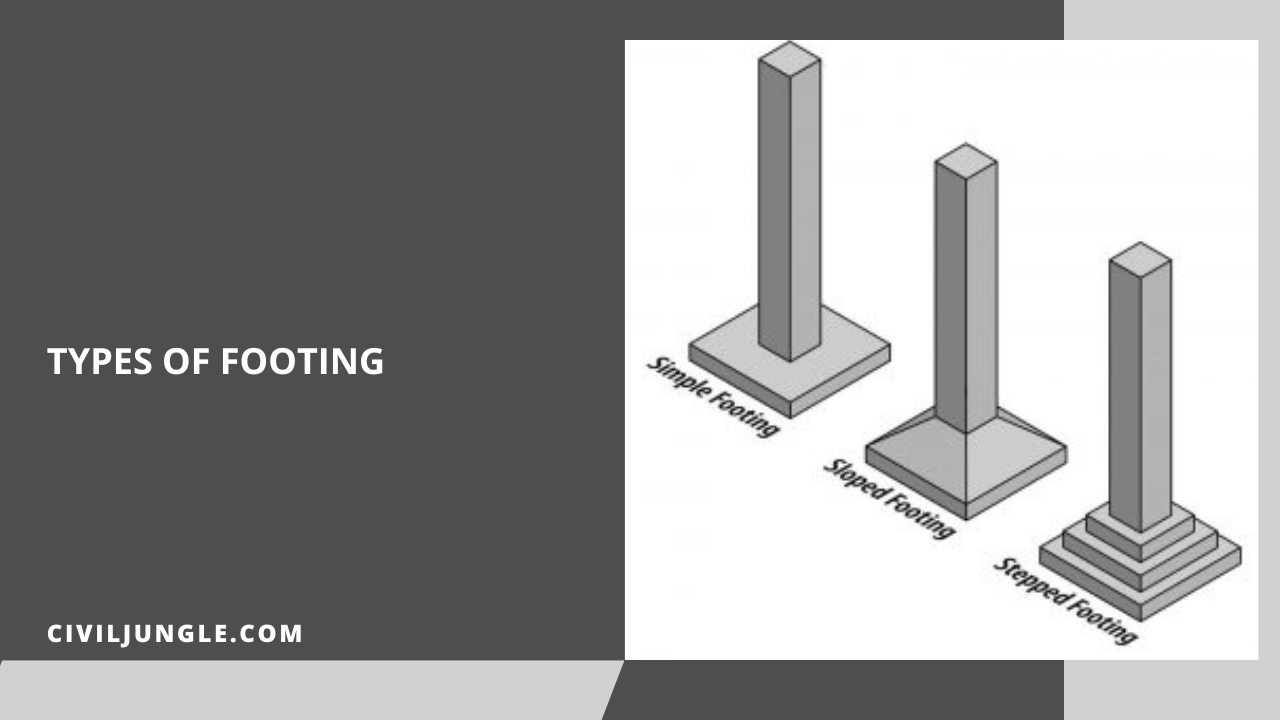
Types of footing
- Isolated Footing:
- Combined Footing:
- Continuous Wall Footing:
- Strap Footing:
- Strip Footing:
- Raft Footing:
- Pile Footing:
- Spread footing
Also, read: Difference Between Lap Length and Development Length
What Is Foundation?
Define Footings: Foundation Engineering, which includes the foundation footing, is a subject built on the basic principles of Soil Mechanics, Soil Hydraulics, and Structural Mechanics.
All these three together may be considered as the pillars of Foundation Engineering.
A wrong application of the principles of any one of the three subjects may lead to a faulty design of the foundation.
Theories have been developed for the design of foundations to suit ideal soil conditions.
However, such conditions rarely exist in nature since soils found in natural conditions are mostly heterogeneous in character.
Theories can have to be modified or adjusted to suit field conditions.
A foundation is a part of a superstructure.
The stresses and strains that are brought to the foundation from the superstructure would lead to interaction between the foundation structural element and the soil surrounding it.
It is this interaction that is very difficult to evaluate, as this is quite a complex phenomenon.
The theories that have been developed for ideal conditions do not take into account all the variables that would lead to the interaction between the soil and the foundation element.
The presence of a water table would make the interaction problem all the more difficult to solve.
It is, therefore, essential that a design engineer should have a thorough knowledge of the theories he wants to use for the design of foundations and also its limitations.
Knowledge of the theories and its limitations by themselves will not lead to the design of a safe and sound foundation if the environmental conditions, the strength and settlement characteristics of the soil are not properly known in advance.
An ideal design engineer, therefore, is the one who has a thorough knowledge of the theories and the field conditions and also who can modify or adjust the design to suit the field conditions.
This requires, therefore, a practical and pragmatic approach to the problem of design and construction while keeping in view the safety and economics of the project.
Also, read: Piling for Foundation | Use of Pile Foundation | Characteristics of Pile Foundation
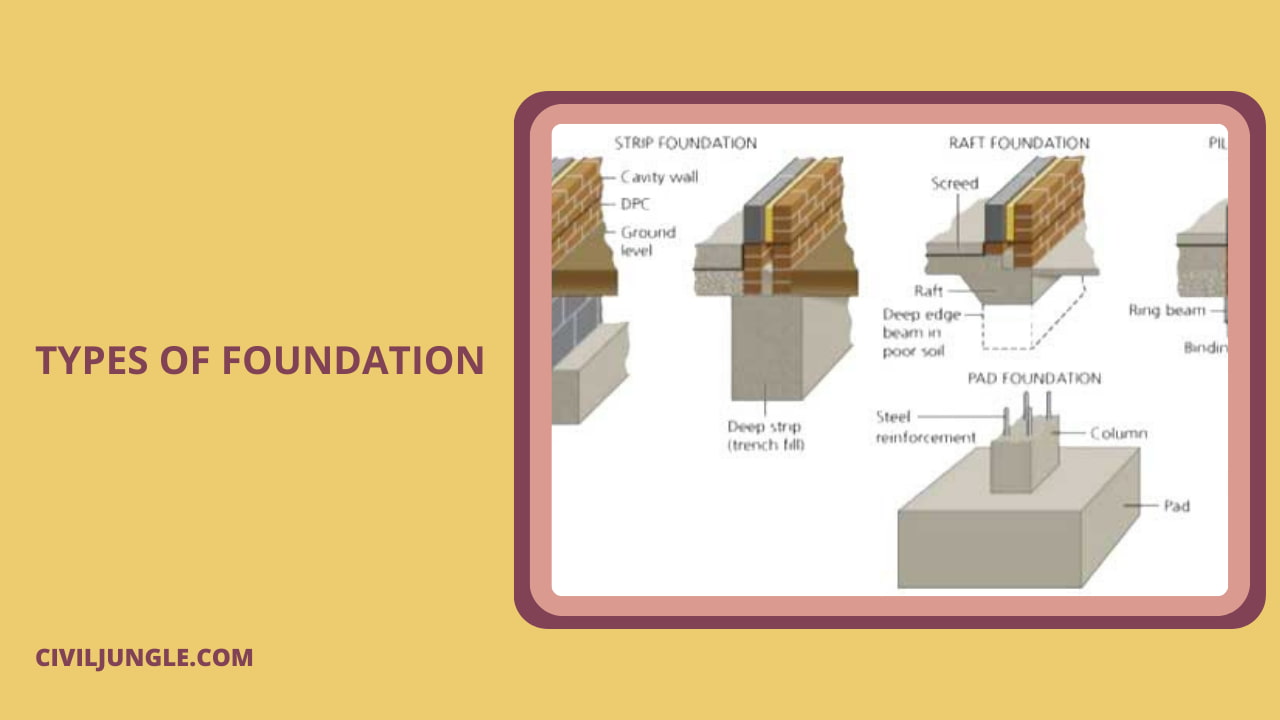
Types of Foundation
Foundation types
- Shallow foundation
- Individual footing or isolated footing
- Combined footing
- Strip foundation
- Raft or mat foundation
- Deep Foundation
- Pile foundation
- End Bearing Pile
- Friction Pile
- Drilled Shafts or caissons
- Pile foundation
Also, read: What Is Guniting, Set Guniting Systems , Advantage, Disadvantage
Difference Between Footing and Foundation
| Sr.No. | Footing | Foundation |
| 1 | The foundation is a general expression for structural elements that supports the superstructure as well as the supporting soil | while the footing is represented the shallow structural element that supports the superstructure. |
| 2 | A formation which is in contact with the ground. | A structure which transfers its gravity loads to earth from superstructure. |
| 3 | A structure which transfers the load from the superstructure to this ground | the foundation which is in contact with the earth. |
| 4 | This is a provides support to the entire building | This provides support to individual columns. |
| 5 | It analogized with the feet of the leg. | It can be analogized with the feet of the leg. |
| 6 | Foundation are of two types, shallow & deep foundation | This footing is a type of shallow foundation |
| 7 | This is the basement of the wall | This is under the foundation wall. |
| 8 | This Footing includes slab, rebar which are fabricated of brickwork, masonry or concrete. | Foundation types include piles, caissons, footings, piers, the lateral supports, and anchors. |
| 9 | Footing reinforces support to an individual column. | this is Foundation is extensive support because it gives support to a group of footings as an entire building |
| 10 | the number of footings repose on a foundation. | This Foundation is the support that bears all kinds of loadings. |
| 11 | This is Footing transmits loads directly to the soil. | This is the foundation is in direct contact with the soil and transmits it to the ground. |
| 12 | All foundations can’t be footing | But all footings are foundations. |
Difference Between Footing and Foundation
The foundation and footing difference is that the foundation is a general expression for structural elements that support the superstructure as well as the supporting soil, while the footing is represent the shallow structural element that support the superstructure.
Continuous Footing
A continuous footing is the one which supports more than two columns. The footing is analogous to the strip footing for a wall. The loads from the individual columns are transferred either directly to the footing slab, or through a longitudinal beam running longitudinally when the loads are heavy.
Is Footing and Foundation Same?
When comparing foundation vs footing, the foundation is a structure which transfers the loads from the superstructure to the ground, while footing is the foundation which is in contact with the earth. A foundation can be shallow and deep, while a footing is a type of a shallow foundation. so, all footings are foundations but all foundations cannot be footings.
What Are Footings and Foundations?
Footings are an important part of footing in construction. They are typically made of concrete with rebar reinforcement that has been poured into an excavated trench. The purpose of footings is to support the foundation and prevent settling. Footings are especially important in areas with troublesome soils.
Suggested Read –
- Stepped Footing
- Cantilever Footing
- Isolated Foundation
- Is 1200 Important Point
- Drilled Piers Foundation
- Type of Stair | Stairs Parts Names & Details
- What Is Lap Length | Lap Length of Column | Lap Length of Slab | Lap Length of Beam
- Detail of Beam Connection | Simple Framing Connection | Semi-Rigid Framing Connection | Rigid Frame Connection
Originally posted 2023-08-22 11:58:03.


Dear Respected Writer, please clarify between How to choose weather that is foundation or footing in construction of base level building.
2. In u r previous constructions building plans why are u mention all 11 colums r F1, don’t we writen as ex. F1,F2,F3…
Q – please clarify between How to choose weather that is foundation or footing in construction of base level building.
Ans – footing part of a residential building, Foundation part of a bridge, flyover etc.
Q – In u r previous constructions building plans why are u mention all 11 columns r F1, don’t we writen as ex. F1,F2,F3…
Ans – F1 = footing 1