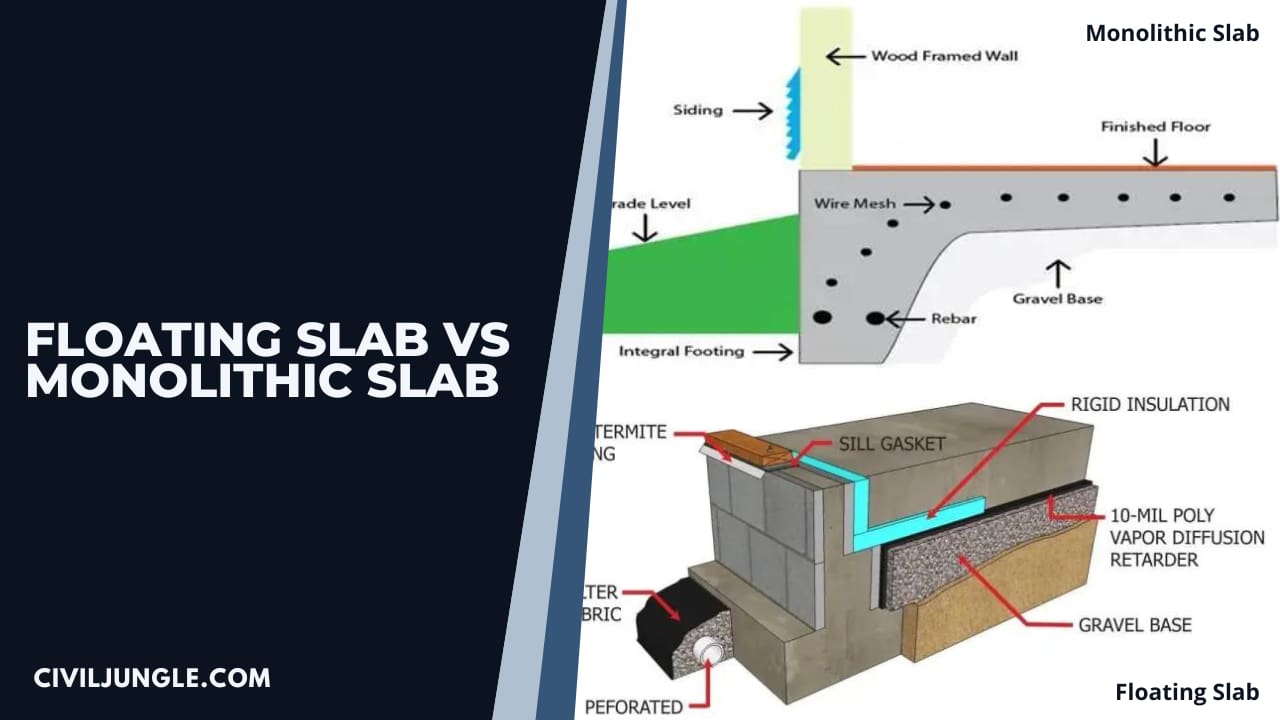
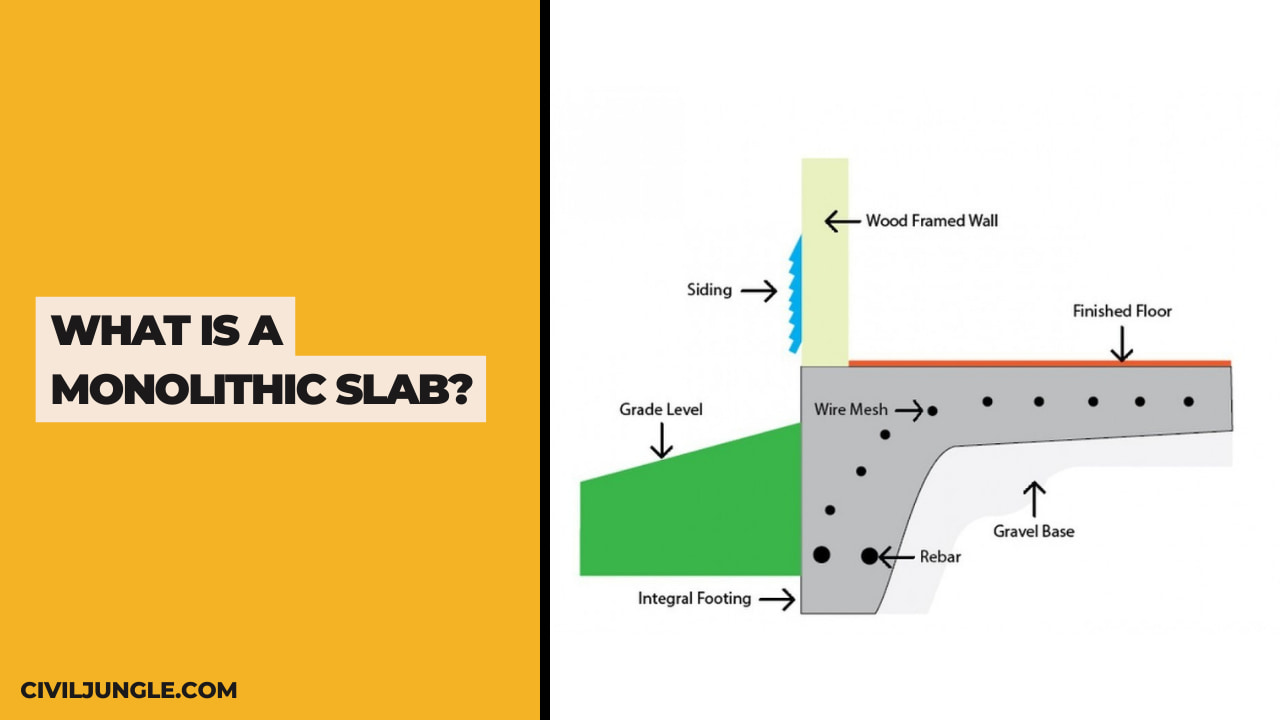
What Is a Monolithic Slab?
Important Point
The word Monolithic means “all in a single pour” so in construction where Monolithic Slab is used the foundation is made in one single pour that is made up of a layer of a concrete slab with thicker area under the load-bearing walls and all the edges of the perimeter to replace the footer.
Construction of Monolithic Slab is much faster and the labor costs are low as in this Slab the concrete is poured all at once. When used under ideal conditions, Monolithic Slab can be just as strong as Stem-Wall slabs.
In most construction of sub-division communities, the ground is levelled and soil is evenly distributed throughout the land which makes the area densely compacted. In this case, Monolithic Slab may be the best option if all the finished floor elevations are the same from lot to lot and there is a very small slope.
There are some major problems that can arise if many conditions are not contusive with the Monolithic Slab. Monolithic Slab cannot be used when more fill dirt is needed because the concrete is more likely to crack if the ground is not compacted sufficiently.
This is a problem for homes that need to be built to rise above the flood plane provided by civil engineers (as most buildings in Florida should).
In this case, the Monolithic Slab tends to crack around the perimeter walls and other large load-bearing areas. These cracks can cause structural problems affecting other aspects of the house while the construction process such as dry walls and floors if the framed walls are not stable.
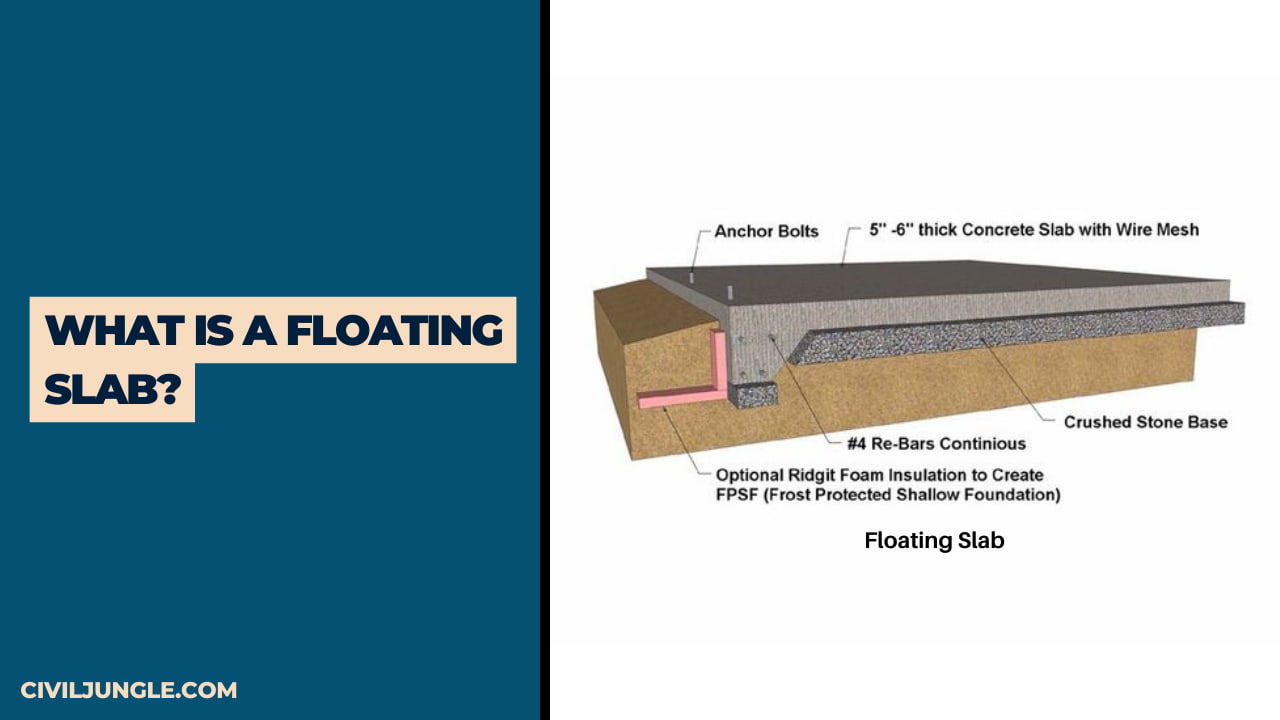
What Is a Floating Slab?
Floating slabs are used as the basis of the foundation for a variety of civil structures like sheds, car garages, additions, cottages, drive sheds, accessory buildings, and barns.
In Floating Slab, the Slabs have a perimeter of thickened reinforced but no frost footings.
Floating Slab are called “floating” because they are allowed to move over the ice line as a monolithic unit. Insulation can also be added to reduce movement due to frost, depending on the needs of the project.
Building a floating slab is one of the most economical ways to build a foundation. Traditional foundations include a strip footing on the edge with a frost wall on top. The strip footing which is placed below the level of frost, usually 4′-0 “below the ground.
The cost of a Floating Slab is higher because there is a lot of excavation, concrete, and labor required for the construction of strip footing and the frost wall.
Floating Slab is the best option for construction of sheds but for construction of house there are some disadvantages to think about.
When Floating Slabs are constructed in a building they can be heated with radiant floor heat which will provide comfortable and balanced heat.
What is a Monolithic Slab VS Floating Slab?
Floating slabs are sometimes called monolithic slabs because they have no contact with the foundation. In some construction floating slab is used as support and only after the foundation has been constructed that we throw the floating slab.
Usually monolithic slab is less expensive than Floating slabs. Floating slabs also happens to be a monolithic slab-shaped as an upside-down U, where concrete is to be applied monolithically or in 2/3 steps. Mono pour which means the way it is built and poured, rather than the kind of the foundation of a building.
If there is a large structure or unstable soil, you definitely want a deep foundation, but with a basic garage in good soil, a floating slab is good and attractive. If the local soil has less stability or as normal water on the subsurface, then the floating slab is very floating, and it is prone to cracking or tilting.
Floating slabs are those lads that float on the ground or in frost areas. Floating slabs are called monolithic slabs in such an environment because they have no contact with the foundation.
Floating Slab Vs Monolithic Slab
The floating slabs are called as monolithic slabs as they have no connection with the foundation. If it’s the case, only after curing of the foundation we cast the floating slab.
What Is a Monolithic Slab?
Monolithic means “all in one pour” so the foundation is constructed in one single pour that is made up of a concrete slab with thicker areas under load-bearing walls and all perimeter edges to take the place of footers. Because this Slab is poured all at once, it is much faster and keeps labor costs low.
Also, Read: What Is Lap Length | Lap Length of Column | Lap Length of Slab | Lap Length of Beam
What Is a Floating Slab?
Floating slabs are used as the foundations for a variety of structures, including sheds, car garages, additions, cottages, and much more. The slabs have a thickened reinforced perimeter but no frost footings. They are called “floating” because they are allowed to move above the frost line as a monolithic unit.
What Is a Monolithic Slab Vs Floating Slab?
Then we have the wall built up above the ground surface. Then literally the floating slabs float on the ground. The floating slabs are called as monolithic slabs as they have no connection with the foundation.
Monolithic Slab
Monolithic means “all in one pour” so the foundation is constructed in one single pour that is made up of a concrete slab with thicker areas under load bearing walls and all perimeter edges to take the place of footers. Because this Slab is poured all at once, it is much faster and keeps labor costs low.
Stem Wall Foundation Vs Monolithic Slab
Monolithic means “all in one pour” so the foundation is constructed in one single pour that is made up of a concrete slab with thicker areas under load-bearing walls and all perimeter edges to take the place of footers. When used under the right conditions, Monoslabs can be just as sound as Stem–Wall slabs.
Monolithic Slab Foundation
A monolithic slab foundation is a type of concrete foundation that is poured in one piece, typically 4-6 inches thick, and serves as both the floor and foundation of a building. It is commonly used in areas with shallow soil frost depths and is known for its durability and efficiency.
Floating Concrete Slab
Floating slabs are concrete slabs that are laying over the ground, without any kind of anchoring, as if it simply sits on it and floats. Floating slab, as the name tells it resembles a plate that is simply laid over water, with no kind of connection between them.
Monolithic Slab Vs Floating Slab
Floating slabs are idle for house addition and garages on the soil with low bearing capacity. In comparison, the monolithic slabs are suitable for the level and well-compacted ground with a low slope.
Floating Slab Foundation
A floating slab foundation is a type of foundation used in building construction. It consists of a concrete slab that is poured directly onto the ground, without any footings or piers, and is not attached to the ground by any means. The slab “floats” on top of the soil, with only a thin layer of gravel or sand between the soil and the concrete.
Monolithic Concrete Slab
A monolithic slab is one whose entire slab is poured as one element and is typically the same thickness across its whole depth. However, depending on the region, the exterior might be made thicker to prevent frost heaving and provide better support for the exterior walls.
Alaskan Slab
One of the simplest and most effective designs is a fairly conventional concrete slab thickened to 18” or 20” at the outside edges and insulated on the outside face. Although based on designs used in Scandinavia for decades, this came to be known as the “Alaska Slab” foundation.
Mono Slab
A monolithic slab foundation is a single, continuous layer of concrete that serves as both the foundation and the floor of a building. The slab is poured directly onto the ground, without any separate footings or foundation walls. The concrete is typically reinforced with steel rebar for added strength and stability.
Monolithic Slab Vs Stem Wall
At DC Builders, we typically offer two types of slab foundations – monolithic slab and stem wall foundations. The primary difference between these options lies in their installation method, as monolithic is poured in one go while stem wall is poured in multiple stages.
Slab Foundation Definition
A slab foundation is made of concrete that is typically 4″ to 6″ thick in the center. The concrete slab is often placed on a layer of sand for drainage or to act as a cushion. Houses built on a slab lack crawlspaces, and there is no space under the floor.
Monolithic Slab Detail
A monolithic slab foundation is a single, continuous layer of concrete that serves as both the foundation and the floor of a building. Here are some common details of a monolithic slab:
- Site Preparation: The site is prepared by grading the soil and ensuring that it is level and stable. The perimeter of the slab is marked, and any necessary plumbing or electrical lines are installed.
- Footings: The perimeter of the slab is excavated to a depth below the frost line and a width of about 12-18 inches. Rebar is installed in the footing trenches, and concrete is poured into the trenches to create a continuous footing around the perimeter of the slab.
Stem Wall Concrete Slab
A stem wall concrete slab is a type of foundation used in building construction that consists of a concrete slab poured on top of a raised perimeter wall (the stem wall). The stem wall is typically made of concrete masonry units (CMUs) or poured concrete and provides additional support and stability for the slab.
Monolithic Slab Foundation Design Example
Here’s an example of a monolithic slab foundation design for a typical residential home:
- Site Preparation: The site is cleared of any debris and leveled to the desired elevation.
- Footings: A continuous footing is poured around the perimeter of the slab, typically 12 inches wide and 6 inches deep.
- Forms: Wooden or metal forms are installed around the perimeter of the slab to contain the concrete.
- Vapor Barrier: A layer of plastic sheeting is placed on top of the soil within the forms to prevent moisture from seeping into the concrete.
- Reinforcement: A grid of steel rebar is installed within the slab area to reinforce the concrete.
- Plumbing: Any necessary plumbing lines, including drain lines and supply lines, are installed in the slab area.
Monolithic Floor
What Is a Monolithic Floor? Monolithic foundations are found with both block and poured walls. The difference is that the floor and footing are poured in one piece instead of two. In other words, the floor is poured with thick edges to it — and those thick edges are the footing.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- What Is Dressing of Stone | Types of Dressing of Stone
- Alignment of Road | Alignment In Design | Horizontal Alignment of Road | Vertical Alignment of Road
- What Is Auxiliary Plane | Types of Auxiliary Plane | Types of Auxiliary View | How to Draw Auxiliary View | Drawing Steps for Auxiliary View
- Well Point System | Types of Well Point System | Well Point Dewatering | PVC Well Point | Well Point Installation | Well Point for Shallow Well
- What Is a Cavity Wall | How to Build a Cavity Wall | Cavity Wall Detail | Cavity Wall Thickness | Cavity Wall Insulation Pros and Cons | Brick Cavity Wall
Originally posted 2023-04-17 18:12:16.


Leave a Reply