Introduction of RQD
Important Point
In Civil engineering, different parameters are used to characterize the Quality of the rocks.
Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties of the rocks and Characteristics of rocks is one of the challenging parts of rock engineering.
Rock mass has wide applications in the construction of structures, excavation and tunnels and maintaining the stable slopes.
Hence, there must be a perfect parameter which is used to evaluate the Quality and the Properties of the rock mass.
RQD is widely used as a crude indicator to evaluate the quality of Rock mass and its properties.
In this article, you will get to know What is RQD and the method of Core Recovery calculation.
Also, read: What Is Workability of Concrete | Factors Affecting Workability | Test |Errors
What Is RQD?
The full form of RQD is Rock Quality Designation which is a parameter used to measure the degree of jointing or fracture in the rock mass.
In simple words, the Rock quality designation is nothing but the measure of the quality of the rock which is obtained from the borehole.
It is generally measured as the percentage of the drill cover in the length of 10cm or more.
The Rock quality designation index was developed by Deere in the year 1964.
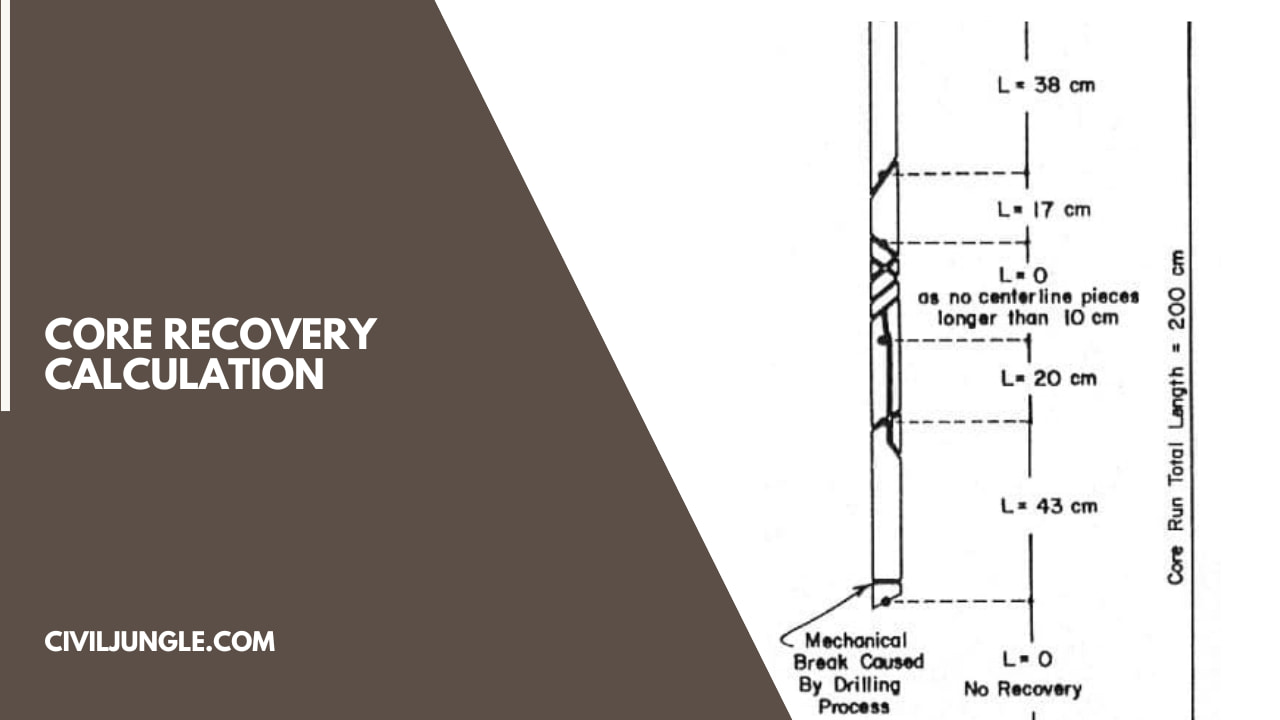
The pieces of Rock are considered which is of hard and good quality. The length of core pieces of Rock mass is measured along the centerline of the pieces
While measuring the index there should not be inconsistency in the measurement.
Also, read: What Is the Penetration Test | What Is the SPT Test | Procedure | Efficiency | Advantages and Disadvantages
Core Recovery Calculation
Core Recovery calculation is done by using the following formula
Rock quality designation is generally calculated by taking the sample of rock mass which is obtained from a borehole.
RQD =[(Sum of the length of core greater than 10 cm) X 100] divided by the total length of the core run
The Rock quality designation (RQD) is generally expressed in the Percentage (%).
In the rock quality designation, the surface is drilled at a certain depth and with the help of the core property of the rock mass is determined.
For determination of Rock quality designation using core boring, the International Society for Rock Mechanics (ISRM) has recommended a core size of at least N X (size 54.7 mm) drilled with double-tube core barrel using a diamond bit.
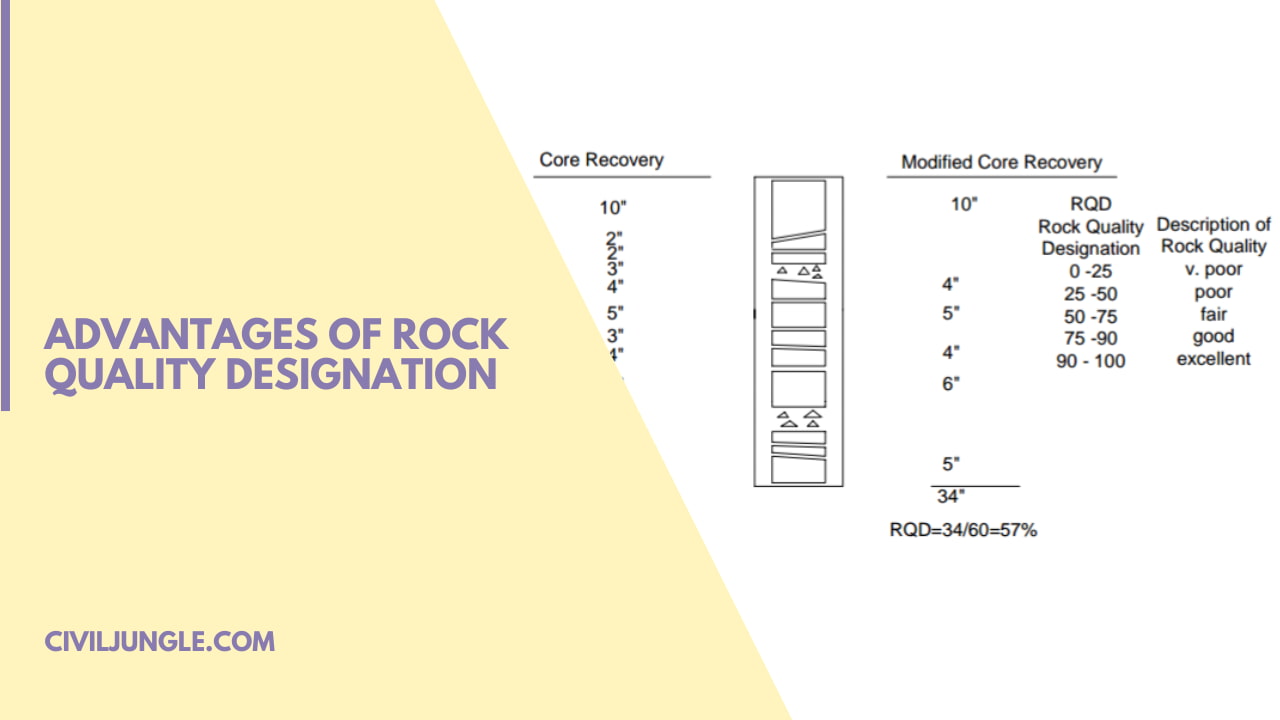
Condition of the Rock as Per There Rock Quality Designation.
| Condition of the Rock |
RQD in % |
| Very poor completely (weathered rock) |
Less than 25% |
| Poor (weathered rock) |
25 to 50% |
| Fair moderately (weathered rock) |
51 to 75% |
| Good (hard rock) |
76 to 90% |
| very good( fresh rocks) |
91 to 100% |
The determination of rock mass strength using the technique of RQD can be performed in the field or the laboratory.
Determination of the deformation modulus and unconfined compressive strength of jointed rock masses is a crucial and challenging part in rock mechanics and rock engineering.
The empirical methods which are based on Rock Quality Designation provide a very convenient way for estimation of the deformation modulus and unconfined compressive strength of rock masses.
In many cases, The Rock quality designation (RQD) is only available data about the discontinuity in the routine site investigation.
RQD is the only factor which affects the deformability and the strength of jointed rock mass.
Also, read: Introduction of USCS | USCS Classifies Soils into Two Broad Categories
Advantages of Rock Quality Designation
- Rock quality designation(RQD) is widely used to check the quality of rocks.
- This test helps to provide an assessment of the soundness of the rocks and the damages which occurred in the rocks due to the action of weathering.
- Rock quality designation(RQD) is also used to evaluate the zones of rock weakness and degree of jointing for fracture in a rock mass.
- It is used to determine the depth of foundation and Bearing capacity of the rock mass.
- Rock quality designation(RQD) is also used to identify the weak rock zones which is very important in the construction of heavy structures.
- The RQD has many applications in mining, engineering geology as well as geotechnical engineering.
- Rock quality designation is also used to obtain the tunnelling conditions.
Limitations of Rock Quality Designation(RQD)
- The Rock quality designation has variable values depending upon the direction of the run.
- Rock quality designation(RQD) does not give in the information of the core pieces which are less than 10 cm.
- Rock Quality Designation gives wrong values where joints contain thin clay fillings or weathered material.
- Does not take direct account of joint orientation.
RQD
Rock-quality designation (RQD) is a rough measure of the degree of jointing or fracture in a rock mass, measured as a percentage of the drill core in lengths of 10 cm or more. High-quality rock has an RQD of more than 75%, low quality of less than 50%. Rock quality designation (RQD) has several definitions.
Rock Quality Designation
RQD is defined as the percentage of intact drill core pieces longer than 10cm recovered during a single core run (Abzalov, 2016), and the general equation is expressed as:RQD index (%)=100×Σ (Length of core pieces≥0.10m)/(Total length of core run)
Rqd Full Form
Rock quality designation (RQD) is a standard technique in the mining industry for the qualitative and quantitative assessment of rock quality and degree of jointing, fracturing, and shearing in a rock mass.
Rqd Formula
RQD forms a basic element in some of the most used rock mass classification systems: Rock Mass Rating system (RMR) and Q-system. RQD is defined as the quotient: % = Sum of length of core pieces that are > 100 mm (4 inches) measured along the centerline.
Rqd Meaning
Rock Quality Designation (RQD) is a measure of quality of rock core taken from a borehole. RQD signifies the degree of jointing or fracture in a rock mass measured in percentage, where RQD of 75% or more shows good quality hard rock and less than 50% show low quality weathered rocks.
What Is Rqd?
RQD stands for Rock Quality Designation. It is a measurement used in geotechnical engineering and geology to assess the quality of rock cores or rock masses. RQD provides an indication of the degree of intactness and continuity of the rock material.
Rqd Calculation
The RQD denotes the percentage of intact rock retrieved from a borehole. All pieces of intact rock core equal to or greater than 100 mm (4 in.) long are summed and divided by the total length of the core run.
What Is Rqd in Geology?
In geology, RQD (Rock Quality Designation) is a parameter used to evaluate the quality and integrity of rock masses. It is specifically measured from drill core samples obtained during geological exploration or engineering projects.
Rock Quality Designation Formula
RFQ is calculated by taking a rock core sample from a borehole and lengths of all sound rock pieces which are minimum 100 mm long are summed up and are divided by the length of the core run.
What Is Rock Quality Designation?
Rock Quality Designation (RQD) is a measurement used in geology and geotechnical engineering to evaluate the quality and integrity of rock masses. It provides a quantitative assessment of the amount of intact or sound rock within a rock sample or a rock mass.
Rqd Calculation Example
Therefore, RQD = (640/1200)x100 = 53% which is fair quality rocks, i.e. rocks are moderately weathered.
Rqd Rock Quality
Rock Quality Designation (RQD) is a quantitative measure used to assess the quality of rock masses in geotechnical engineering and geological studies. It provides information about the degree of intactness and soundness of the rock material within a sample or a rock mass.
Rqd Classification
Rock Quality Designation (RQD) can be used as a basis for classifying rock masses into different categories based on their quality and integrity. The classification systems may vary depending on the specific application or engineering field. One commonly used classification system that incorporates RQD is the Rock Mass Rating (RMR) system developed by Bieniawski.
What Does Rqd Mean?
RQD is calculated as a percentage and is derived from the lengths of intact and sound rock pieces larger than a specified size (usually 10 cm or 4 inches) within a rock sample or core. These intact rock pieces should be relatively free from fractures, weathering, or other significant defects.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- What Are Bridge Abutment | Types of Abutments
- What Is Fresh Concrete | Properties of Fresh Concrete
- Difference Between CPM and PERT | What Is CPM & PERT
- What Is Falsework | Types of Falsework |Causes of Falsework Failures
- What Is Gypsum Plaster | Advantage and Disadvantage of Gypsum Plaster
- Difference Between Formwork, Shuttering, Centering, Staging & Scaffolding
Originally posted 2023-06-20 16:25:39.





Leave a Reply