Weight of 4″, 6″, 8″, 10″ and 12″ Solid & Hollow Concrete Block
Important Point
There are two primary concrete block categories: hollow and solid. Both of these concrete block types are typically used during the construction of walls but are used for other purposes.
Two main types of concrete blocks are used in the construction industry: hollow and solid. Substantial blocks are often used for projects such as paving, where stability and durability are essential.
A concrete masonry unit made of a mixture of concrete, cement, sand, and water is known as CMU. Concrete masonry units are in the form of concrete blocks, concrete bricks, hollow concrete blocks, solid concrete blocks, lintel blocks, concrete stretcher blocks, concrete pillar blocks, split concrete blocks, corner concrete blocks, and concrete pillar blocks.
Hollow blocks, which have holes that cover one-fourth and usually more than half of their cross-sectional area, are used to construct boundary fences and other large structures. The holes make them lighter and can be helpful when running wiring or piping.
The hollow concrete blocks: Hollow concrete blocks come in three grades.
- Grade A has a minimum density of 1,500 kg/m3.
- Grade B thickness is less than 1,500 kg/m3.
- Grade C thickness is more significant than 1,000 kg/m3.
Grades A and B are used for load-bearing concrete block walls, while grade C is used for load-bearing walls.
Also Read: Understanding Concrete PSI: How Many Bags of 3000 PSI Mix for Your Project?
Hollow Blocks Come in Many Types.
1. Stretcher Block:
Concrete stretcher blocks are used in construction to connect the corners of masonry units.
2. Column Block:
Pillar blocks are used to make pillars. They are also called double-corner blocks, which are designed in such a way that both ends are visible. And they are usually available in large quantities at building supply stores.
3. Lintel Block:
Also called channel or beam blocks, lintel blocks are recognizable by their U shape. Deep grooves made by a U shape running along the length of these blocks are filled with concrete and reinforcing bars. Like the one pictured here, concrete-bottom lintel blocks are purchased in 6-by-8-by-16-inch configurations.
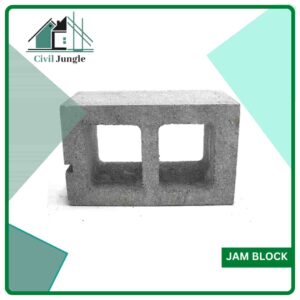
4. Jam Block:
Two holes in the jam block have a shallow groove and a deep groove at one end. They provide space for window casing members and are often used in double-hung windows.
Also Read: How Many 8×8×16 Blocks on a Pallet?
5. Column Block:
A column block is usually a square block with a hole. Thus these are stacked to form columns with internal reinforcement.
6. Corner Block:
Corner blocks are placed at corners, as you might expect, or with the plain side in contact with the outside at the window and door ends, while the straight side runs parallel to the wall.
7. Split-Face Block:
This block is highly porous and, therefore, susceptible to water damage, but it is less prone to termite infestation and fire. Splitface blocks look like pillar blocks, but along the edge, they have a rough, almost uneven surface that exposes the internal capacity of the league.
8. Bullnose Block:
Single bullnose blocks are similar to corner blocks in their use and construction, except they have rounded edges that account for their name.
Also Read: How Much Do Cinder Blocks Weigh?
A Split Block:
Split blocks are identical to concrete column blocks, except they are taller than wide. Viewed directly, these narrow blocks look almost like wide glasses.
The Solid Concrete Block:
Fine concrete blocks look like gray bricks but are more expansive. Solid concrete block is heavier than hollow but less expensive. They are suitable for building walls that protect against the factors such as strong winds.
It is used for garden walls and plantings, retaining walls, and foundations; The same is done for projects like steps and firepits.
Solid blocks come in many types.
Fly ash blocks: Fly ash is a fine, powdery material that mixes with water to form a material similar to Portland cement. Crystal color can be amber, brown, gray, green, olive, red, yellow, or yellow-brown.
The resulting color can vary depending on the aggregation of the particles but is often brown. Portland cement is made by mixing limestone, clay, or shale that has been finely ground or burnt.
Fly ash bricks only come in small sizes because the larger they are, the more durable they are, and larger sizes are more prone to fracture and cracking.
There are two classes of fly ash:
Class C is a high calcium variety that contains less than 2% carbon. It can range from 15% to 40% of the cement content.
Class F has a 5% to 10% carbon content and is low in calcium. It usually makes up 15% to 25% of the cement content.
The use of fly ash can reduce CO2 emissions, provide resistance to cold weather, and reduce cracking problems and permeability. It can also create smooth, detailed surfaces in one go.
Pneumatic autoclave blocks: These lightweight concrete blocks contain 80% air, meaning “air-entrained.” Pneumatic autoclave blocks, compact AAC blocks, are lightweight materials with high sound and temperature insulation.
These blocks are white to light gray and are suitable for use in sidewalls, partition walls, and other types of wall construction, as well as steel piers and infill panels.
Its fire resistance and insulating properties make it an attractive option, although it is less widely available than other solid forms. They are available in blocks of various thicknesses, discussions, and unique shapes, such as lintels and U-shaped bond beam blocks.
Paving block: Paving blocks are square or rectangular concrete blocks used for paving, on road shoulders where they are painted to improve visibility, and in walkways.
Although often brick-shaped, they are available in various sizes and colors, including sandstone, tan, dark brown, charcoal, and light brown.
Cellular Lightweight blocks: The lightweight cellular block is a building material that consists of three components: foam, fly ash, and cement. It is fire-resistant, environmentally friendly, and relatively inexpensive.
These light gray blocks are made from one such material. Like AAC, it provides good insulation against noise and extreme temperatures. It is customizable, made in various sizes, and is used for wall panels, composite walls, and parapet walls.
A total block of expanded clay: Expanded clay aggregate blocks consist of lightweight fly ash and cement aggregates. Waterproof and fire resistant, their lightweight nature allows them to reduce overall structural weight by up to 50%.
They also insulate well against noise and temperature. Because this material is fired in a kiln, it is molded into different shapes with different densities.
A typical 4-inch solid cinder block weighs 33 pounds or 15 kilograms. That’s more than a full-size 6-inch block and about the same as a standard 8-inch block. A 10″ wide cinder block weighs between 35 and 44 lbs.
Also, read Erosion Control by Concrete Blocks. These load-bearing units shall have a minimum block density of 1500 kg/m3. Production of concrete blocks minimized.
Typically, concrete masonry units have nominal face dimensions of 8 inches 203 mm by 16 inches 406 mm, available in nominal thicknesses of 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16 inches.
A typical 8-inch or 8 x 8 x 16 hollow 2-cored cinder block weighs about 38 pounds (17 kg ), depending on its application. But the most common, nominal sizes of concrete block used are 4″, 6″, 8″, 10″ and 12″ CMU full/half blocks.
They are known by the depth or thickness of the wall they form. For example, a 6″ CMU is typically 6″ or 150mm deep, while a 10″ CMU is typically 10″ or 250mm deep.
Widely used in many parts of the world, including India, the USA, the UK, and other countries, Concrete Masonry Units (CMU) are manufactured in various sizes.
How much does a concrete block weigh: A typical 8-inch or 8 x 8 x 16 hollow two-core concrete block weighs about 38 pounds 17 kilograms, while a precisely solid 8″ x 8″ x 16″ concrete block weighs about 76 pounds.
- A 2″ x 8″ x 16″ concrete block weighs about 17 pounds (7.7 kg).
- A 4″ x 8″ x 16″ hollow concrete block weighs approximately 32 pounds (14.5 kg).
- A 6″ x 8″ x 16″ hollow concrete block weighs about 25 pounds (11.34 kg).
- A 10″ x 8″ x 16″ hollow concrete block weighs about 43 pounds (19.5 kg).
- A 12″ x 8″ x 16″ hollow concrete block weighs about 52 pounds (23.5 kg).
What is the weight of a solid concrete block: According to the UK, concrete blocks or breeze blocks can weigh from 19 kg to 38 kg or 2150 kg/m3 or 134 lbs/ft3.
A full-size standard 100mm thick solid concrete block weighs approximately 19kg, a 150mm thick block weighs 27kg, and a 200mm thick block weighs 36kg.
- 4″ full-size CMU solid concrete blocks can weigh 17kgs or 37.5 lbs.
- 6″ full-size CMU solid concrete blocks can weigh 25kgs or 55 pounds.
- 8″ full-size CMU solid concrete blocks can weigh 34kgs or 75 pounds.
- 10″ full-size CMU solid concrete blocks can weigh 42kgs or 93 lbs.
- 12″ full-size CMU solid concrete blocks can weigh 50kgs or 110 lbs.
What is the weight of a hollow concrete block: Hollow concrete block density or unit weight varies between 1100 kg/m3 to 2150 kg/m3 or 69 lbs/ft3 to 134 lbs/ft3.
- A 4″ full-size CMU / hollow concrete block can weigh 8.8kgs to 17.2kgs or 19.4 to 38 pounds.
- A 6″ full-size CMU/hollow concrete block can weigh 13.2kgs to 25.8kgs or 29 to 57 pounds.
- An 8″ full-size CMU/hollow concrete block can weigh 17.6kgs to 34.4kgs or 38.8 to 76 pounds.
- A 10″ full-size CMU/hollow concrete block can weigh 22kgs to 43kgs or 48.5 to 95 pounds.
- A 12″ full-size CMU/hollow concrete block can weigh 26.4kgs to 51.6kgs or 58 to 114 pounds.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –









Leave a Reply