What are Traps In Plumbing?
Important Point
As the name suggests, traps simply trap the water and sewer gas. A trap is a plumbing device used to prevent smell, bacteria, also insects entering your home.
Every water-using appliance or fitting has a drain line to flow out the waste-water, and you must have a trap in the pipe that seals the drain.
The seal is important to keep the environment fresh as it will prevent sewer gasses from entering the building. You can see traps equipped with varied plumbing fixtures like sinks, bathtubs, toilets, and washbasin.
With the help of several connections, you can install a trap which is usually located within a plumbing fixture.
Traps are designed in such a way that it retains some amount of water which indeed creates a seal for foul gasses and stops them from entering the property.
Also, read: Crushing Strength Test, Water Absorption Test, Abrasion Test, Impact Test, Acid Test
What Does Trap do?
Traps are designed to prevent sewer odors from entering the home through the plumbing fixtures. The seal in the trap is provided by the waste-water.
Every time we use a fixture, we flush out the water that is forming the trap seal and replace it with new water.
Traps are carefully engineered systems. They are designed to be self-scouring so that they don’t collect debris yet retain water to form a seal. The velocity with which waste moves through a trap is important.
If it’s too fast, the water that is supposed to remain in the trap will be siphoned down the drain. If it’s too slow, solids will tend to get deposited in the bottom of the trap.
It’s easy to see why people shouldn’t try making their own traps out of piping and fittings.
Types of Traps in Plumbing
Different types of traps in plumbing are as follows.
- Floor Trap or Nahni Trap.
- Gully Trap.
- P Trap.
- Q Trap.
- S Trap.
- Intercepting Trap.
- Bottle Trap.
- Grease Trap.
- Drum Trap.
- Running Trap.
- Straight-Through Trap.
- Low-Level Bath Trap.
- Bell Trap.
- Building Trap.
Also, read: Requirements of Good Building Stones
1. Floor Trap:
This trap is provided on the floor to collect wastewater from the bathroom, sink, shower, and washbasin, etc. These are available in UPVC or cast iron material and have removable grating on the top of the trap. The minimum depth of the water seal should be 50 mm, 75mm, 110mm.
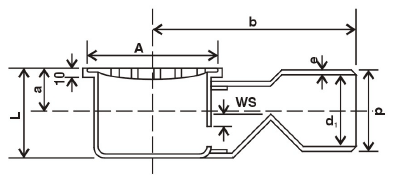
2. Gully Trap:
Gully Trap, also known as G.T. A Gully Trap, is provided outside the building before connecting it to the external sewerage line. It also collects wastewater from the kitchen sink, washbasins, bath, and wash area.
The heavy cast iron gully traps shall not be less than 7.25 KG in weight with cover weighing not less than 4.53 kg, and frame not less than 2.72 kg, and total depth shall not be less than 30 cm (1 ft) also available UPVC gully trap As per figure.
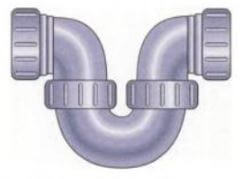
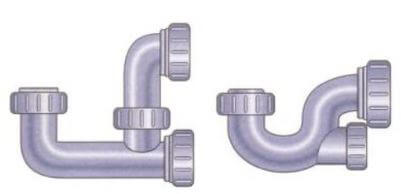
3. P Trap:
This trap is used with an Indian water closet. The traps are made from UPVC or cast-iron sheets. This trap also has a water seal and prevents entry of foul gases to the house.
4. S Trap :
This trap is similar to the P. trap and is used for fixing water closets in toilets. The only difference between the P trap and the S trap is that the P trap is used for an outlet through the wall, whereas S-trap is used for an outlet through the floor.
5. Q Trap:
This trap is used in a toilet under-water closet. It is almost similar to the S trap and is used in the upper story other than the ground floor.
Also, read: Types of Flooring.
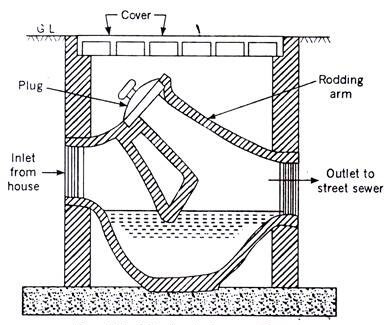
6. Intercepting Trap:
The intercepting trap is provided to the Interceptor Manhole. An Interceptor manhole is provided at the interception of Public sewer and building sewer.
Intercepting trap is provided to prevent the foul gases from public sewers entering into the building sewer by providing water seal. Designed with a deep water seal of 100 mm, these traps are installed at the last main hole of building sewerage.
7. Bottle Trap:
In this type of trap, the waste pipe is fitted horizontally, and you need to unscrew the bottom to clean it. Ideal to be installed in limited spaces, the bottle traps are widely utilized at pedestal mounted sinks and basins to trap foul gasses.
Also Read: Types of Locking Washers
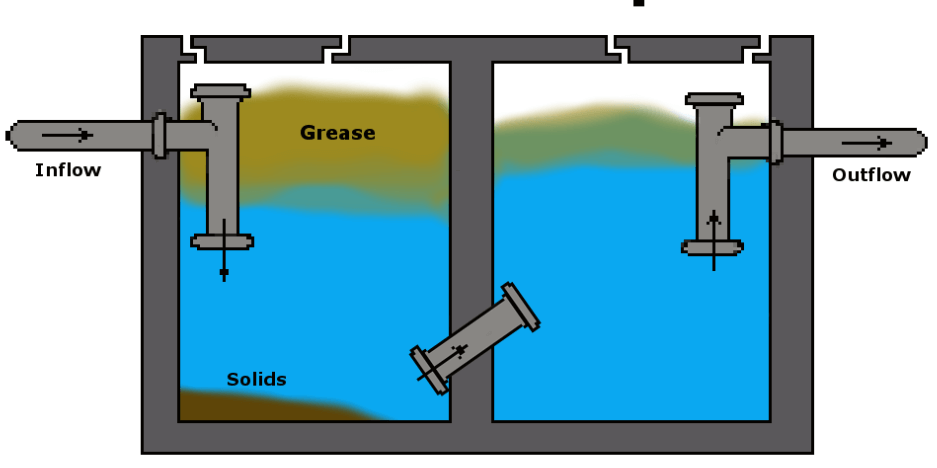
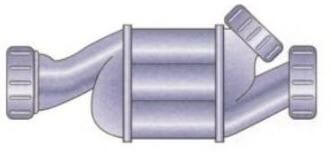
8. Grease Trap:
These traps are highly useful for food processing units as the trap is specially designed to collect grease content, and it is very easy to clean these traps from the surface.
The design works effectively to intercept the most grease and solid contents, entering a wastewater disposal system.
Since these traps are used to reduce the amount of fats and oils entering the main sewer, these traps can be found at commercial cooking facilities.
9. Drum Trap:
Drum traps, which resemble metal drums, are an important part of a home plumbing system because their large openings allow you to more easily locate and remove objects you need either to retrieve or to remove from the plumbing system.
Their large caps also allow you to easily insert into the trap a plumbing snake you can use to remove clogs in your drain.
Water from a drainpipe in your home flows into the trap from the trap bottom, then exits at the top of the trap, leaving solid objects behind in the trap.
Because water always remains in the trap, blocking sewer gases from leaking into your home through this trap.
Also, read: What Are Walls
10. Running Trap:
You might see these used in public toilets where one running trap is used for a range of untrapped washbasins. On domestic installations, it could be used where a P or S trap arrangement is not possible.
Running traps are sometimes used with a washing machine waste outlet or for dishwashers, although specialist traps are available for these appliances.
11. Straight-Through Trap:
These are used as an alternative to a trap where space is limited. They are also easier to hide behind pedestal basins. The main problem with this design is the two tight bends, which slow down the flow of water shown above figure.
An alternative valve works on the simple principle of using an internal membrane as a seal, shown above figure. The membrane allows water to flow through it when the water is released, then closes to prevent foul air from entering the building.
The valve can be used on systems meeting BSEN 12056 – Part 2. It is ideal for fitting behind pedestals and under baths and showers and is supplied with a range of adaptors so that it can be used in various situations.
The valve has the potential to revolutionize the installation of above-ground systems, the requirements of which will be covered in the next section.
System-design procedures for the straight-through trap will be covered fully at Level 3.
12. Low-Level Bath Trap:
These are designed so that they can fit into tight spaces under baths and shower trays. The seal on these will only be 38 mm, which means they cannot be connected directly into the soil and vent stack.
13. Bell Trap:
Bell Trap Drain is designed for use in the garage, patio, or other outdoor use. The water drains into a well in the drain unit that serves as a trap to contain sewer gas. The strainer snaps onto the drain body. 1 in. By 2 in. Bell Trap Drain fits over 1 in.
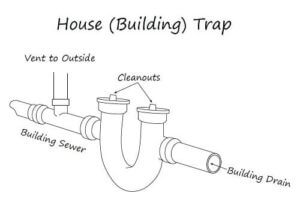
14. Building Trap:
Not to mention the sewer gas odor could be unbearable because of backpressure and trap siphonage. Health officials knew that this could pose a serious health risk, especially in heavily populated, wet, and dry areas.
Therefore, to combat the issues above a house, a building trap is required in each building. The building trap provided a secondary line of defense against the vermin and sewer gas. Most times, the building trap was a large diameter S-trap.
Nahni Trap
Nahni trap is also called as Floor Trap (Nahni in hindi means washing/bathing place). Nahni Trap is provided to prevent the foul gasses entering into the building by providing the water seal. Whether waste water is flowing or not, floor trap prevents the foul gases (bad smells) to enter in to the building
Floor Trap
Floor trap is also called as Nahni Trap (Nahni in hindi means washing/bathing place). Floor Trap is provided to prevent the foul gasses entering into the building by providing the water seal. Whether waste water is flowing or not, floor trap prevents the foul gases (bad smells) to enter in to the building
Gully Trap
A gully trap is a basin in the ground which receives piped wastewater from inside your home before it is emptied into the wastewater network. The basin has a water seal to prevent foul odours of the sewer reaching the surface, and a vent pipe that allows fresh air in.
P Trap
The p–trap traps water in its dip, sealing off the pipe. … This water eliminates space for any air or gases to flow back up through the drain. As you can see, water is the main factor that allows a p–trap to work. If the p–trap becomes dry, then those smells can start to seep into your building.
S Trap
A trap is simply a configuration of the drain pipe underneath a sink or any other plumbing fixture. S-traps are no longer used in modern plumbing because the water can be sucked completely out of the trap allowing sewer gas to enter your home.
Running Trap
Running traps (or building traps) are traps located in the drainage piping that are not directly connected with a fixture. Many older homes had running traps in the building sewer, typically in the front lawn. These traps were designed to prevent sewer gases from entering the house.
Building Trap
The building trap is a U-shaped bend in the main sewer drain as it leaves your home. The purpose of this trap was to hold, or “trap” water and create a barrier between the putrid methane atmosphere of your city’s sewage system and your home. This is usually known as the “U-bend” or “P-trap”.
Types of Trap
Different types of traps are as follows.
- Floor Trap.
- Gully Trap.
- P Trap.
- S Trap.
- Q Trap.
- Intercepting Trap.
- Bottle Trap.
- Grease Trap.
- Drum Trap.
- Running Trap.
- Straight-Through Trap.
- Low-Level Bath Trap.
- Bell Trap.
- Building Trap.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- What Is Plaster | Type of Plaster | Defects In Plastering
- Difference Between One Way Slab and Two Way Slab | What is Slab
- Difference Between Bitumen and Tar | What Is Bitumen | What Is Tar
- Introduction of Gantry Girder | Load on Gantry Gutter | Type of Load on Gantry Gutter
- What Is Pier Foundation | Types of Drilled Piers | Advantages and Disadvantages of Drilled Pier Foundations









Leave a Reply