Introduction to Levelling
Important Point
Levelling is one of the most important parts of surveying before starting the construction of roads, dams, or any other structures.
It is a branch of surveying which deals with the measurement of the elevation of the point with respect to the datum level above or below the surface of the ground.
In this article, you will get to know about the Types of levelling in surveying, the advantages, and disadvantages of levelling.
What Is Levelling in Surveying?
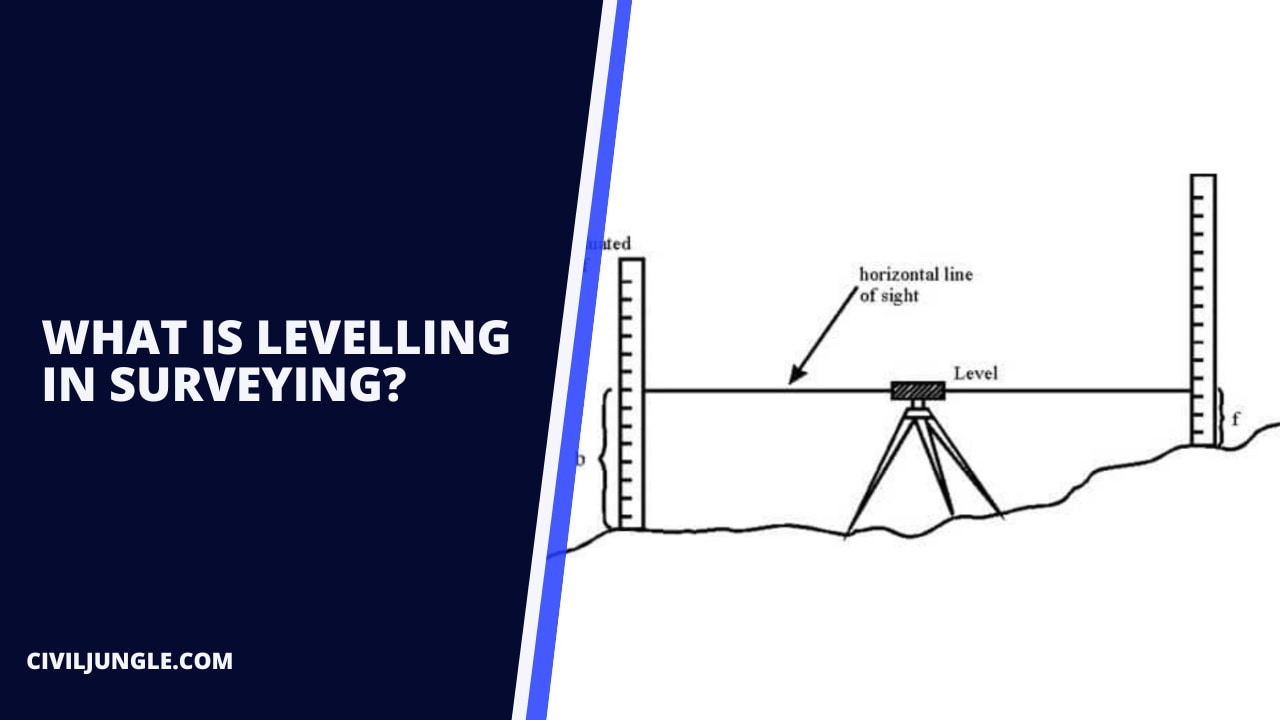
Levelling is defined as the art of determining the relative heights or the elevations of different points on the surface of the earth so that the same may be represented on a plan or map. Levelling process mainly deals with the measurements in the vertical plane.
Levelling is a process of taking the measurement of the level of the ground in the vertical plane.
Principle of Levelling
The principle of levelling is to obtain a horizontal line of sight with respect to the vertical distances of the points above or below this line are found.
Objective of Levelling
The objectives of levelling are as follows.
- The main objective of levelling is to determine the elevation of given points with respect to some reference line which is known as Datum.
- To establish different points at required elevation with respect to Datum.
Necessity of Levelling.
- Levelling process has a prime importance before carrying out any kind of construction on site.
- Levelling is used for acquiring the data for designing of roads, canals, railways, buildings, dams, bridges, and water supply systems.
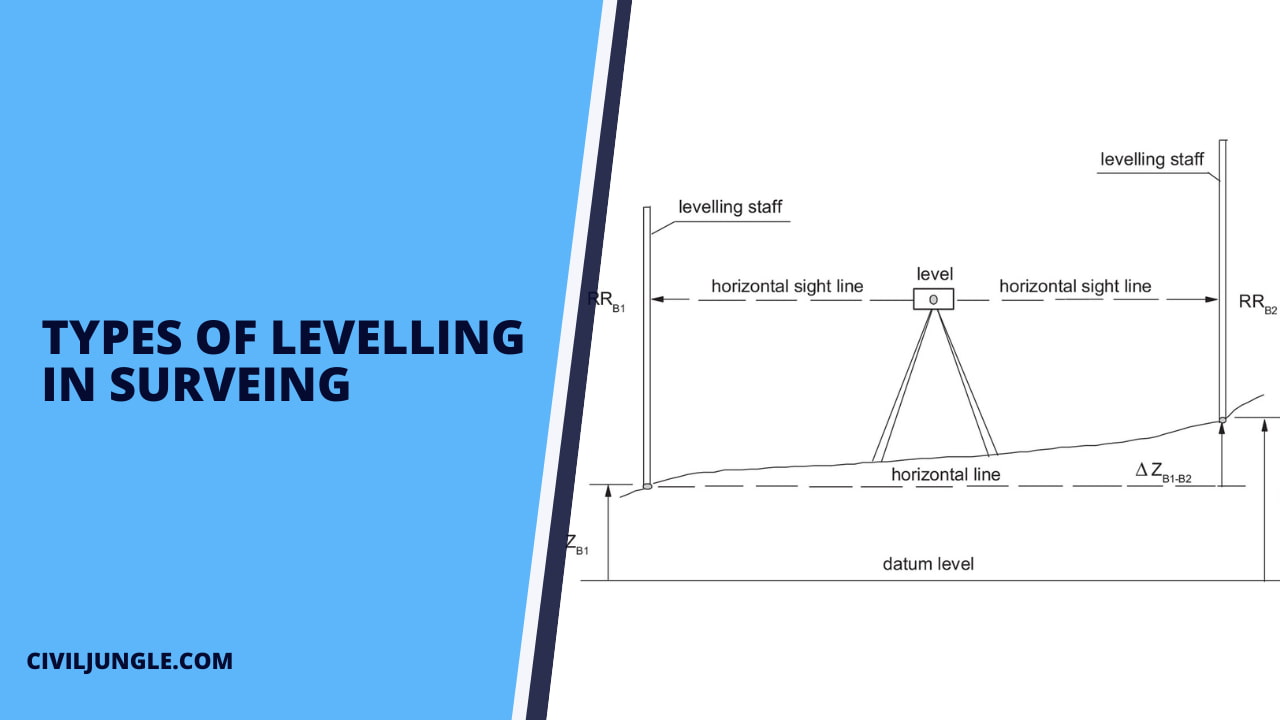
Types of Levelling in Surveying
The Types of levelling which are used in surveying are as follows.
- Barometric Levelling.
- Trigonometric Levelling or Indirect Levelling.
- Spirit Levelling or Direct Levelling.
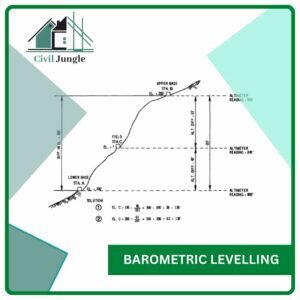
1. Barometric Levelling
Barometric levelling is defined as the levelling which makes use of the phenomenon that the difference in the elevation between the two points which are located at different places is proportional to the difference in the atmospheric pressure at these points.
The Barometer instrument is used for measuring the difference in the elevation between the two points on the surface of the Earth is an old and well-known art.
The Barometer instrument is used to measure Atmospheric pressure at any altitude. This type of levelling is rarely used in surveying work. Barometric levelling is generally used for reconnaissance or exploratory surveys.
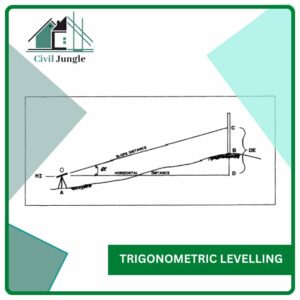
2. Trigonometric Levelling
Trigonometric levelling is one of the simplest process of levelling in which the elevation of the points is determined from the vertical angles and the horizontal distances which are measured on the field.
Trigonometric levelling is also known as Indirect levelling. It is the same as the length of any side of the triangle is determined from the basic trigonometric relations.
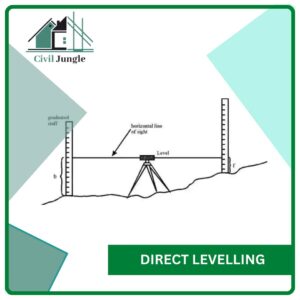
3. Direct Levelling
It is the most commonly used method of leveling. In this method, measurements are observed directly from leveling instrument.Based on the observation points and instrument positions direct leveling is divided into different types as follows:
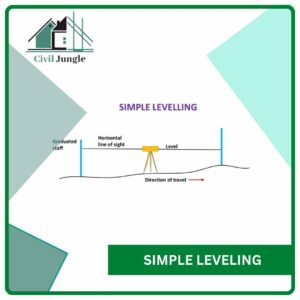
3.1. Simple Leveling
Simple levelling is a very easy process that consists of calculating the difference in the elevation between two points. The instrument is set up between the two points so that both points are visible.
The distance between the two points should not be too greater otherwise it is difficult to take the readings from both points. The Simple levelling process is only suitable when the points are closer to each other without any kind of obstacles between them.
The procedure of the simple leveling are as follows.
- Suppose, there are two points on the ground surface let it be A and B.
- The instrument can be set up at anywhere but it is recommended to set the instrument approximately at the midway between the two points so as to eliminate the errors in the instrument.
- Then level the instrument carefully and direct the telescope towards the staff which is held vertically at point A and focus it.
- Take the readings at which the horizontal hair appears to cut the staff. Now hold the staff vertically at point B.
- Direct the telescope on the staff which is held vertical at the point and focus it properly. Take the readings on point B and care should be taken that the bubble should be at the centre while taking readings.
While carrying out the levelling process the following point should be considered.
- The care should be taken that the bubble should be in the centre while taking readings.
- If the true difference of the level between the two points is required then it is necessary that the instrument should be set up exactly mid between both the points.
- When the point is on the lower elevation the staff reading is greater and when the point is on higher elevation the staff reading is smaller.
- When the staff is held at the lower point then the staff reading will be greater and the reduced level is less. If the staff point is on the higher point then the staff reading will be smaller and the reduced level is more.
Also, Read: 15 Difference Between Plastering And Pointing | What Is Plastering | What Is Pointing
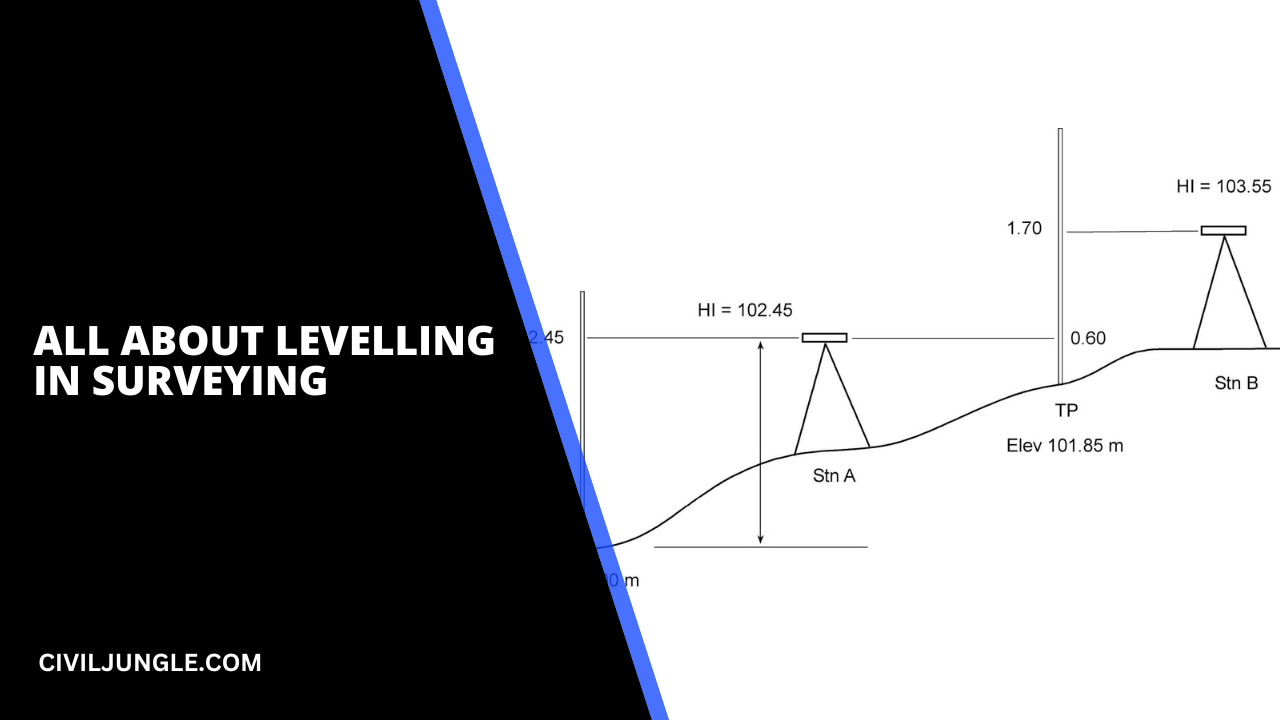
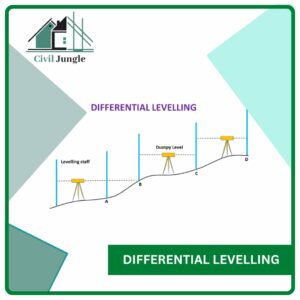
3.2. Differential Levelling
The differential levelling is used in surveying when it is required to determine the difference in the elevation between the two points which are too far apart from each other and the difference in the elevation between that two points is far great.
Differential levelling is used when there are some obstacles in levelling so that the points are not visible from one setup of the instrument. So it is necessary to set up the instrument at various locations and to work in a series of the stages.
The differential levelling process is suitable when the distance between the two points is more.
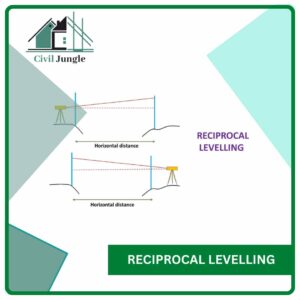
3.3. Reciprocal Levelling
Reciprocal levelling is used when it is required to find an accurate difference in the level between the two points which is considerably apart from each other.
The reciprocal levelling process is used when it is not suitable to setup the level between the two points due to any obstacle such as a river or pond etc.
The reciprocal levelling eliminates the error due to curvature and collimation. It also eliminates the error due to the line of collimation.
In this case, the instrument is set up on both sides of the bank of the river or valley and two sets of staff readings are taken by holding the staff on both banks.
Also Read: Levelling Surveying
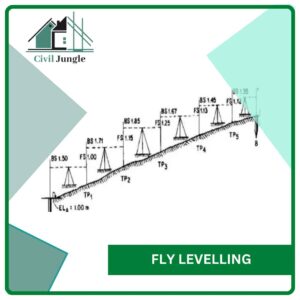
3.4. Fly Levelling
Fly levelling is the process in which only the backside and foresight readings are taken and there are not any intermediate sight readings are taken in this type of levelling.
The purpose of the fly levelling is to connect the benchmark to the starting point of any project and it is used to establish the benchmarks.
The process of Fly levelling is used when the worksite is away from the benchmark. In this case, the surveyor starts the work with the back sight reading on the benchmark by setting up the instrument at a suitable point.
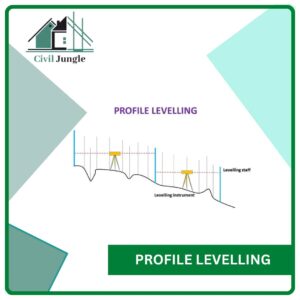
3.5. Profile Levelling
Profile levelling is the process of determining the elevation of the points at short measured intervals along a fixed line such as the centre line of a railway, highway, canal or sewer.
The fixed-line may be a single straight line or it make consists of a succession of the straight lines. It is also known as longitudinal sectioning.
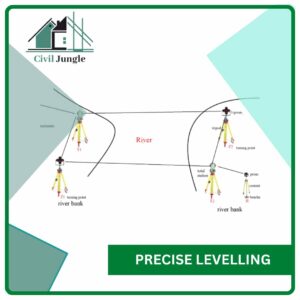
3.6. Precise Levelling
It is a type of levelling in surveying which is used for establishing the benchmarks with very high precision at widely distant points. This type of surveying is conduct by the government agencies such as the great trigonometrical survey of India department for establishing the benchmarks.
This kind of levelling required a highly refined and modern instrument which should be operated by the skilled technical person only.
Also, Read: Top 10 Cement Companies in USA
3.7. Check Levelling
It is basically a method that is used to check a series of levels or readings which have taken previously. At the end of each day work ok a line of level starting from the point and returning to the starting point is checked.
Advantages of Levelling in Surveying
There are various advantages of levelling in surveying are as follows.
- Levelling helps to determine the elevation of the points on the surface of the ground.
- It is helpful while laying the centerline of the road.
- The data which is obtained from the process of levelling helps to understand the terrain of the ground.
- Levelling is very useful for designing structures.
Disadvantages of Levelling in Surveying
There are also some disadvantages of levelling in surveying which are as follows.
- The levelling process is very time-consuming.
- Levelling process required a skilled and Technical person.
- To plot the levels on the map or sheet is a very complex process and required a lot of calculations.
What Is Levelling in Surveying?
Leveling is a process to determine the vertical position of different points below, on, or above the ground. In surveying operations, vertical elevations and vertical control are generally derived independently of horizontal control.
Principle of Levelling
The principle of levelling is to obtain horizontal line of sight with respect to which vertical distances of the points above or below this line of sight are found. Terms used in levelling Datum “It is an arbitrary level surface from which elevation of points may be referred”.
Objective of Levelling
The main purpose of levelling in surveying are: To find the elevations of given points with respect to a given datum. To establish points at given elevations or different elevations with respect to the given or assumed datum.
Advantage of Levelling in Surveying
It help the surveyor or cartographer to make contour maps of the land sea surface. this is because it determine the benchmark. It help pipe transport engineers to ensure appropriate slope of the land that will allow smooth movement of the liquid in the transit e.g water and liquid.
Precise Levelling Techniques
There are three leveling techniques: differential, trigonometric, and barometric. Differential leveling is the most accurate of the three methods. With the instrument locked in position, readings are made on two calibrated staffs held in an upright position ahead of and behind the instrument.
Advanced Levelling Instruments
Advanced leveling instruments are sophisticated tools that offer enhanced precision, accuracy, and efficiency in the leveling process. These instruments incorporate advanced technologies to streamline the surveying workflow and improve the quality of measurements. Here are some examples of advanced leveling instruments used in modern surveying:
- Automatic Level: Automatic levels, also known as self-leveling levels, are commonly used in surveying and construction. These instruments feature a built-in compensator that automatically levels the line of sight, ensuring accurate measurements even if the instrument is not perfectly level. Automatic levels are easy to use and provide rapid measurements, making them suitable for various leveling applications.
- Digital Level: Digital levels are equipped with electronic sensors and display units, offering precise and direct measurements of elevations. These instruments eliminate the need for manual reading of graduated staffs, reducing human errors. Digital levels often have additional features such as data storage, data transfer capabilities, and built-in software for data processing, enabling efficient data management and analysis.
- Laser Level: Laser levels utilize laser technology to project a highly visible laser beam, creating a horizontal or vertical reference line. They are commonly used for applications such as transferring levels, aligning and leveling building elements, and setting out slopes.
Digital Levelling Technology
Digital leveling technology refers to the use of digital instruments and electronic sensors to perform leveling tasks in surveying. Digital leveling instruments have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their numerous advantages over traditional analog leveling instruments.
Levelling Accuracy Standards
Leveling accuracy standards refer to the accepted levels of precision and accuracy that should be achieved in leveling measurements. These standards provide guidelines for surveyors and ensure consistency and reliability in surveying and construction projects. The accuracy standards for leveling measurements can vary depending on the specific application and the desired level of precision.
Differential Levelling in Surveying
Differential leveling is the most accurate of the three methods. With the instrument locked in position, readings are made on two calibrated staffs held in an upright position ahead of and behind the instrument. The difference between readings is the difference in elevation between the points.
What Are the Advantages of Levelling?
Following are the advantages of levelling: Levelling helps to prevent soil erosion caused by wind or air. It helps in sowing the seeds uniformly, and thus helps the plants to grow uniformly too. It helps in proper irrigation by allowing the water to get distributed uniformly throughout the soil.
Define Levelling
Leveling is a fundamental technique used in surveying and engineering to determine the relative heights or elevations of different points on the Earth’s surface. It involves measuring vertical distances or differences in elevation between benchmark points, reference points, or survey points. The primary objective of leveling is to establish a level or horizontal line of sight, which serves as a reference for measuring vertical distances.
What Is Levelling?
Levelling is a surveying technique used to determine the relative heights or elevations of different points on the Earth’s surface. It involves measuring vertical distances or differences in elevation between benchmark points, reference points, or survey points. The primary goal of leveling is to establish a level or horizontal line of sight, which serves as a reference for measuring vertical distances.
What Is Levelling in Surveying?
• Levelling or leveling is a branch of surveying, the object of which is to establish or. verify or measure the height of specified points relative to a datum. • It is widely used in cartography to measure geodetic height, and in construction. to measure height differences of construction artifacts.
Why Is Levelling Important?
Leveling is important because gravity is by far the most significant force in the durability and function of buildings. Working parallel and perpendicular to the force of gravity is fundamental in designing and constructing buildings regardless of their shape.
Types of Levelling in Surveying
Types of Leveling in Surveying
- Direct leveling.
- Trigonometric leveling.
- Barometric leveling.
- Stadia leveling.
Level Surface in Surveying
Level surface is the continuous surface parallel to the mean spheroid of the earth. The line representing the level surface is termed as level line. The level line makes right angles to the vertical line or plumb line at any point. It means the any point on level line is equidistance from the center of earth.
What Is Profile Levelling in Surveying?
In short, profile leveling refers to the process of determining the elevation of points on the ground at mostly uniform intervals. along a continuous line.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Spillway Types
- Types of Levelling
- Pile Cap Design Guide
- Different Types of Rollers
- Top 10 Cement Companies in USA
- Top 10 Best Cement Companies In India 2021
- Top 10 Bathroom Fittings & Sanitary Brands India
- What Is Grouting | Types of Grouting | Advantage of Grouting
- What Does Parapet Mean | Types of Parapet Wall | Uses of Parapet Wall
- Cinder Block Vs Concrete Block | What Is Cinder Blocks | What Is Concrete Blocks
Originally posted 2023-06-12 15:30:01.



Leave a Reply