What Is Viscosity?
Important Point
Viscosity may also be termed as a drag force and is a measure of the frictional properties of this fluid. Temperature and pressure function of Viscosity.
Though the viscosities of both liquids and gases vary with pressure and temperature, they affect the viscosity in another manner.
Within this book, we’ll deal primarily with a viscosity of fluids and its change as a function of temperature.
Viscosity is expressed in two distinct forms:
- Dynamic viscosity
- Kinematic viscosity
What is Dynamic Viscosity?
Dynamics of fluid flow, often referred to as dynamic and kinematic viscosity, is the study of fluid motion, including the forces causing flow. Viscosity (Dynamic) is defined as the resistance offered to a layer of fluid when it mores over another layer of fluid.
Rate of shear stress is directly proportional to the velocity gradient. Dynamic viscosity is flowed the newton 2nd Law (Second law) as per newton second law of motion. He says which relates the acceleration with the forces.
Due to the force exerted on the material, the deformation causes the fluid-fluid particle to move. Science ‘fluid’ Kinematics viscosity, studying only motion without thinking of force.
This chapter presents the first primary discussion of the science of fluid force fluid dynamics and its practical and general application.
A clear concept of force and acceleration is necessary to understand the speed of the transmission. According to Newton’s law of motion (Newton’s Second Law of Motion),
force (force) = Mass X Acceleration
f = m.a (F=Force, M= Mass, A = Acceleration)
It is usually the practice of using m (Mass) in the pursuit of force for a solid. But the Greek letter p is used for fluid-fluid particulars.
Acceleration is used only for acceleration or for acceleration. The actual force applied to a particular solution according to Newton’s rule – net force, Its product of force and acceleration is equal to – product.
Thus the fluid has viscosity – viscosity. But to develop equations of motion, the equation is considered inviscid – inviscid.
In reality, no true view is devoid of real fluid. But other factors such as pressure force – pressure force and gravity force –
Since the viscous effect is insignificant relative to the gravitational force, it can be ignored, and in doing so, there is no possibility of major impairment.
One fact should be noted that in some cases, the force of prudence may also be important. For example, glycerin cannot be ignored when a fluid flows into a narrow tube or flows between two adjacent surfaces.
Since airtightness is extremely low in air motion, it can be easily ignored, but the fact that air is compressible cannot be ignored.
Assuming that the pressure of convection is caused by gravitational force, the equation can be written as follows (Dynamic Vs. Kinematic Viscosity).
Actual tension force on gravity + gravitational force = volume of force x its acceleration Net pressure force on a fluid particle + net gravity force on a fluid particle = particle mass x particle acceleration.
τ = µ x du/dy, where µ represents the dynamic viscosity formula
- du/dy = constant of proportionality
- µ = Dynamic viscosity
- τ = Coefficient Euler’s equation of motio
Also read :What is Bulkage of Sand?
Equation of Motion
-
Euler’s equation of motion
(1/p) x (dp/ds) = -v x (dv/ds)
-
- p = Density of fluid
- dA = Cross-sectional area of this fluid element
- ds = Length of this fluid element
- dW = Weight of this fluid element
- P = Pressure on this element at A
- P+dP = Pressure on this element at B
- v = velocity of This fluid element
-
Bernoulli’s equation from Real Fluid
P+(1/2).p.v.v +p.g.h = Constant
-
- P = Pressure on the element at A
- p = Density of fluid
- v = Velosity
- h = elvation
- g = gravitational elevation
What Is Kinematic Viscosity?
Kinematic viscosity, often asked as kinematic viscosity is defined as, is the ratio of the dynamic viscosity (mass viscosity) of a fluid. Mathematically,
Kinematic viscosity ∝ = Dynamic viscosity (µ) / Density (δ)
- ∝ = Kinematic viscosity
- µ = Dynamic viscosity
- δ = Density
Using the kinematic viscosity formula, we have ∝ = µ / δ.
Topics related to acceleration and types of motion, etc. are discussed. An initial discussion of the equation for pressure and total force and pressure center due to the viscosity properties and the static mass.
It also moves due to a very small amount of learner stress on the visual. Likewise, the motion is also due to the slight imbalance in the membrane pressure on the visual.
Useful Article For You
- Types of Grillage Foundation
- Types of Doors
- Types of Hinges
- Types of Columns
- Types of Cranes
- Types of Shovels
- Paint Types
- Roof Material Types
- Types of Buildings
- Roof Tiles Types
- Types of Construction Vehicles
- Types of Concrete
- Types of Tables
- Roof Vent Types
- Types of Sand
- Types of Walls
- Types of Washers
- Types of Kitchen Sinks
- Types of Scaffolding
- Meaning Types of Road Markings
- Types of Plumbing Pipes
- Types of Retaining Walls
- Types of Pavers
- Types of Driveways
- Types of Paint Brushes
- Types of Floors
- Types of Curves
- Closet Door Types
- Types of House Foundations
- Concrete Finish Types
- Water Valve Types
- Paint Types for Walls
- Different Types of Couches
- Types of Stucco
- Types of Curtains for Windows
- Types of Beams
- Types of Stairs
- Types of Hard Hats
- Types of Grout
- Types of Porches
- Types of Bay Windows
- Types of Traps
- Types of Concrete Blocks
- Types of Vaulted Ceilings
- Types of Corrosion
- Types of Plumbing Fittings
- Types of Sewer Pipe
Type of Kinematic Viscosity Flow:
- Steady and unsteady flows.
- Uniform and non-uniform flows.
- Laminar and turbulent flows.
- Compressible and incompressible flows.
- Rotational and irrotational flows.
- One, two, and three-dimensional flows.
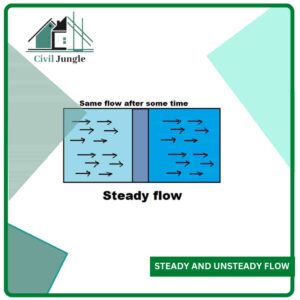
1. Steady and unsteady flow:
u,v,w=0 dv/dt=0 dv/ds =0
-
- dv= change of velocity
- dt = time
- ds = length of flow in the direction S
Unsteady flow: type of flow in which the fluid properties changes with time.
dv/dt ≠ 0 dv/ds =0
-
- dv= change of velocity
- dt = time
- ds = length of flow in the direction S
Also, read : SOUNDNESS OF CEMENT TEST
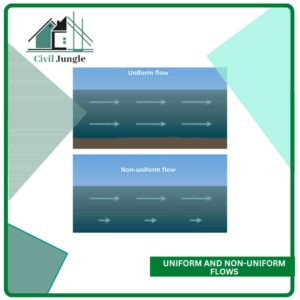
2. Uniform and non-uniform flows:
dv/ds = 0, dp/ds = 0
-
- dv = change of velocity
- dt = time
- ds = length of flow in the direction S
Non-Uniform: velocity, pressures, density, etc. at give time change with respect to space
dv/ds ≠ 0, dp/ds =0
Also, read : CORE CUTTER METHOD
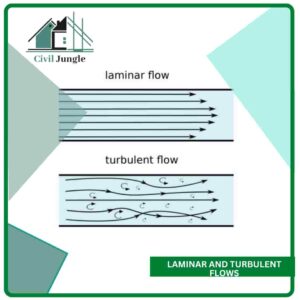
3. Laminar and turbulent flows:
- Laminar flow is also called viscous flow or stream,
- This type of flow is only possible at slow speed and in a viscous fluid
Turbulent flow: in which fluid particles more irregularly and disorderly, i.e., fluid particles move in a zig-zag way. The zig-zag irregularly of fluid properties is responsible for high energy loss.
Also, read: IS CODE FOR CIVIL ENGINEER [Q&A]
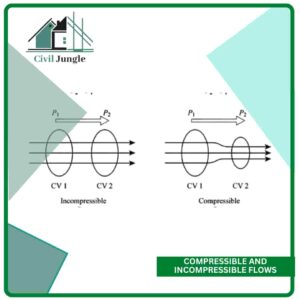
4. Compressible and Incompressible Flows:
Thus, mathematically, for compressible flow
p ≠ Constant
Incompressible flow: Type of flow in which the density is constant fluid flow. Liquids are generally incompressible then gases are compressible.
Mathematically, for incompressible flow
p = Constant.
Also, read : LAB TEST ON AGGREGATES AT SITE
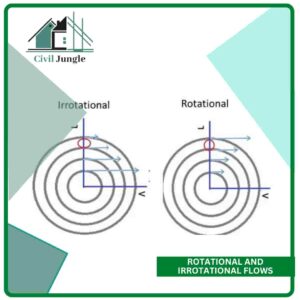
5. Rotational and Irrotational Flows.
Irrotational Flows: Fluid particles while flowing along stream-lines, not rotate about their own axis then that type of flow is called irrotational flow.
Also read: PROCEDURE FOR RCC CONCRETE
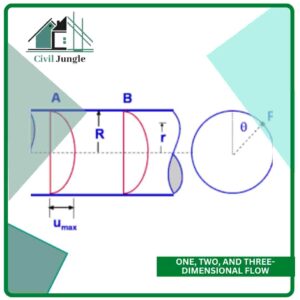
6. One, Two, and Three-Dimensional Flow:
 One-dimensional:
One-dimensional:
- This is the flow in which the flow parameter such as velocity is a function of time, and one space co-ordinates only, say axis X.
- For a steady one dimensional flow in direction, the velocity is a function of one-space and co-ordinate only.
- The variant of velocities in additional two mutually perpendicular directions is assumed negligible.
- Hence mathematically, for one-dimensional
flow u =f( x), v = 0 and w = 0
- Where u, v and w are velocity components in x, y and z directions respectively.
Two-dimensional flow:
- That kind of flow in which the velocity is a function of time and two rectangular space co-ordinates say x and y.
- For a steady two-dimensional flow, the velocity is a function of two space coordinates only.
- The variation of velocity in that third direction is negligible.
- Thus, mathematically for two-dimensional flow
u = fi(x, y), v = f2(x, y) and w = 0.
Three-dimensional flow:
- That kind of flow where the velocity is a function of time and also three mutually perpendicular directions.
- However, to get a constant three-dimensional stream, the fluid parameters are functions of three space coordinates (x, y, and z) only.
- Thus, mathematically, for three-dimensional flow
u = fi(x, y, z), v = f2(x, y, z) and w = f3(x, y, z).
Dynamic Viscosity Vs Kinematic
When comparing dynamic viscosity vs kinematic viscosity, we note that dynamic viscosity is a measure of fluid’s resistance to shear flow when some external force is applied. Kinematic viscosity is ratio of dynamic viscosity to density of that fluid. It is measure of fluid’s resistance to shear flow under the weight of gravity.
What Is the Difference Between Kinematic and Dynamic Viscosity?
The difference between dynamic and kinematic viscosity is that kinematic viscosity incorporates fluid density as part of its measurement. Thus, dynamic viscosity is a measure of force, while kinematic viscosity is a measure of velocity. That’s the difference. If you divide kinematic viscosity by the fluid density, you get absolute viscosity.
What Is the Formula of Kinematic Viscosity and Dynamic Viscosity?
Using the kinematic viscosity equation, the formula for the conversion is: Kinematic (cSt) x Density = Dynamic (cP). Dynamic (cP) / Density = Kinematic (cSt)
Dynamic Viscosity
The dynamic viscosity η (η = “eta”) is a measure of the viscosity of a fluid (fluid: liquid, flowing substance). The higher the viscosity, the thicker (less liquid) the fluid; the lower the viscosity, the thinner (more liquid) it is.
Dynamic Vs Kinematic Viscosity Units
The unit of dynamic viscosity is Pa s. Usually, it is measured in centipoise (cP). Kinematic viscosity is expressed as the ratio of fluid dynamic viscosity to its density. The unit of measurement of kinematic viscosity is m2s-1.
Kinematic Viscosity and Dynamic Viscosity Formula
Dynamic viscosity is the resistance to movement of one layer of a fluid over another and is defined by Formula F7. 8. Kinematic viscosity is dynamic viscosity divided by density (Formula F7. 9) and is the ratio of viscous forces to inertia forces.
Kinematic Viscosity Formula
The formula for kinematic viscosity is given by the ratio of absolute viscosity to the density of the fluid. It is denoted by the symbol v. Its unit of measurement is newton seconds per meter square (Ns/m2), and the dimensional formula is given by [M1L-1T-1].
Dynamic Viscosity Units
Dynamic viscosity: The SI physical unit of dynamic viscosity (μ) is the Pascal-second (Pa s), which is identical to 1 kg m−1 s−1. The physical unit for dynamic viscosity in the centimeter gram second system of units (cgs) is the poise (P), named after Jean Poiseuille.
Dynamic Viscosity of Water
The dynamic viscosity of water is 8.90 × 10−4 Pa·s or 8.90 × 10−3 dyn·s/cm2 or 0.890 cP at about 25 °C. Water has a viscosity of 0.0091 poise at 25 °C, or 1 centipoise at 20 °C. where A=2.414 × 10−5 Pa·s ; B = 247.8 K ; and C = 140 K.
Dynamic Viscosity Symbol
The symbol for absolute (dynamic) viscosity is mu: µ (although eta η is also sometimes used).
Dynamic Viscosity of Air
The viscosity of air depends mostly on the temperature. At 15 °C, the viscosity of air is 1.81 × 10-5 kg/(m·s) , 18.1 μPa·s or 1.81 × 10-5 Pa·s .
Dynamic Viscosity Formula and Unit
The units of dynamic viscosity are: Force / area x time The Pascal unit (Pa) is used to describe pressure or stress = force per area This unit can be combined with time (sec) to define dynamic viscosity. Pa•s for use in calculations.
Kinematic Viscosity Unit
Kinematic viscosity has SI units of m2 s−1. The physical unit for kinematic viscosity is the stokes (St), named after George Stokes. It is sometimes expressed in terms of centistokes (cS or cSt); 1 stokes = 100 centistokes = 1 cm2 s−1 = 0.0001 m2 s−1.
Kinematic Viscosity Symbol
nu: ν
The symbol for kinematic viscosity is nu: ν and its SI units are m/s2.
Absolute Viscosity Unit
poise
The poise (symbol P; /pɔɪz, pwɑːz/) is the unit of dynamic viscosity (absolute viscosity) in the centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS). It is named after Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille (see Hagen–Poiseuille equation). The centipoise (1 cP = 0.01 P) is more commonly used than the poise itself.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Build Up Area Definition
- Consistency Test of Cement
- Introduction of Gantry Girder | Load on Gantry Gutter | Types of Load on Gantry Gutter
- What Is Dry Pack Mortar | Advantages of Dry Pack Mortar | Disadvantages of Dry Pack Mortar
- What Is Unit Weight | What Is Density | What Is Unit Weight Material | Unit Weight Building Materials
- What Is Pier Foundation | Types of Drilled Piers | Advantages and Disadvantages of Drilled Pier Foundations
- What Is Diversion of Headworks (Rivers) | Types of Diversion Headworks | Component Parts of Diversion Headworks (Rivers)

Wonderful post but I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject, thanks!
If you want to improve your knowledge only keep visiting this website and be updated with the most recent news update posted here.
Your article is really helpful. thnks…