What is Lap Length?
Important Point
Lap Length is required when bars placed short of their required length (due to nonavailability of longer bars) need to be extended.
- Lap Length is also required when the bar diameter has to be changed along the length (as is sometimes done in columns).Branding
The purpose of ‘Lap’ is to transfer the axial force effectively from the terminating bar into the connecting bar with this same line of action in the junction.
This invariably introduces stress concentrations at this surrounding concrete. These effects should be minimized by
- Using proper splicing techniques.
- Keeping these lapping locations away from sections with high flexural/shear stresses. and
- Staggering the locations of splicing at the individual bars of a group (as typically in a column).
When splicing in such situations becomes unavoidable, special precautions need to be employed, such as
- Increasing the length of the lap (In lap splices and lap welding)
- Using spirals or closely-spaced stirrups around the length of the stirrups.
Lap Length As Per IS 456
Generally, development length is 41d where d is the diameter of the bar. For direct tension, the lap length should be 2 Ld or 30d whichever is greater is considered. In this case, the straight length of the lapping bar shall not be less than 15d or 20cm.
Also, read: What Is Lintel | Type of Lintel
Type of Lapping Method:
- Lapping of bars (lap splice)
- Welding of bars (welded splice)
- Mechanical connection.
1. Lap Splices
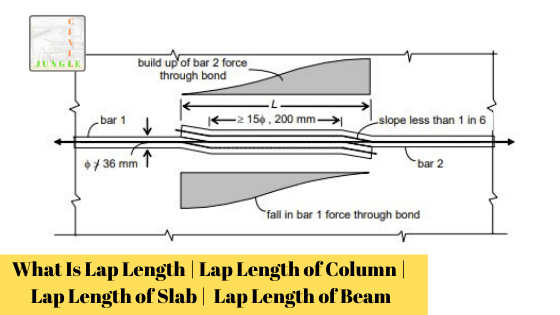
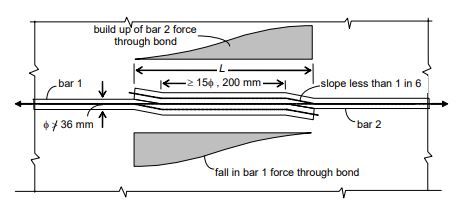
Lap splices are achieved by overlapping this bars over a certain length, thereby enabling this transfer of axial force from the terminating bar into the connecting bar through the mechanism of anchorage (development) bond with the surrounding concrete (As per below fig)
A) Lap splice action through development bond
The splitting and cracking behavior observed in lap splice tests are found to be similar to those in anchorage bond tests (As per below fig).
B) Use of spirals in lap splices for large diameter bars
The Lap splices are usually not permitted for very large dia. Bars (Ø > 36 mm), for which welded splices are recommended. However, where welding is not practicable, the Code (IS Code 456-200 Page No- 45, Cl. 26.2.5.1a) permits lap splices with additional spirals around the lapped bars (As per below fig).
C) Staggered splicing of bars
It is desirable to bend the bars slightly (particularly large diameter bars) near the splice location in order to ensure a collinear transfer of force (without eccentricity), as shown above, fig A.
The Code specifies that the straight length of the lap should not be less than 15Ø or 200 mm.
As the force transfer is through development bond, the lap length should at least be equal to the development length Ld.
The Code (IS Code 456-200 Page No- 45, Cl. 26.2.5.1c) specifies a lap length of 2Ld in situations where the member is subjected to direct tension.
In no case should the lap length be less than 30Ø under flexural or direct tension and 24φ under compression.
When bars of two different diameters are to be spliced, the lap length should be calculated on the basis of the smaller diameter.
Splices in tension members shall be enclosed in spirals made of bars not less than 6 mm diameter with the pitch, not more than 10mm.
In the revised Code, some additional clauses have been incorporated (IS Code 456-200 Page No- 45, Cl. 26.2.5.1c) to account for the reduction in bond strength with regard to rebars located near the top region.
When lapping of tension reinforcement is required in the top of a beam (usually near a continuous support location or a beam-column junction), and the clear cover is less than twice the diameter of the lapped bar, the lapped length should be increased by a factor of 1.4.
If the rebar is required into turn around a corner (as in an exterior beam-column junction), the lapped length should be increased by a factor of 2.0.
This factor can be limited to 1.4 in the case of corner bars when the clear cover on top is adequate, but this side cover (to the vertical face) is less than twice this dia. of the lapped bar.
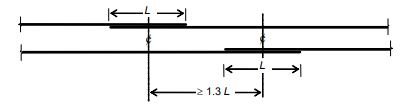
When more than one bar requires splicing, care must be taken to ensure that the splicing is staggered, with a minimum (center-to-center) separation of 1.3 times the lap length, as indicated in as per above fig (c).
It is also desirable to provide (extra) transverse ties (especially in columns), connecting the various longitudinal bars in the spliced region.
In the case of bundled bars, the lap length should be calculated considering the increased Ld, and the individual splices within a bundle should be staggered.
- Methods of Design | Difference Between Working Stress Method and Limit State Method
- Load Calculation on Column
2&3. Welded Splices and Mechanical Connections
Welded splices and mechanical connections are particularly suitable for large diameter bars.
This results in reduced consumption of reinforcing steel. It is desirable to subject such splices to tension tests in order to ensure the adequacy of strength
Welding of cold-worked bars needs special precautions owing to the possibility of a loss in strength on account of welding heat.
The Code (IS Code 456-200 Page No- 45, Cl. 26.2.5.2) recommends that the design strength of a welded splice should, in general, be limited to 80 percent of the design strength of the bar for tension splices.
Butt welding of bars is generally adopted in welded splices. The bars to be spliced should be of the same diameter.
An additional two or three symmetrically positioned small diameter lap bars may also be provided (Especially when the bars are subjected to tension) and fillet welded to the main bars.
Even in the case of ‘lap splices,’ lap welding (at intervals of 5φ) may be resorted to in order to reduce the lap length. End-bearing splices are permitted by the Code (IS Code 456-200 Page No- 45, Cl. 26.2.5.3) for bars subject to compression.
This involves square cutting the ends of this bars and welding the bar ends to suitable bearing plates that are embedded within the concrete cover.
Also, read: What Is Raft Foundation | Type of Footing | Detail of Raft Footing
Bars Bundled in Contact of Reinforcement
The development length of each bar of bundled bars shall be that for the individual bar, increased by 10 percent for two bars at contact, 20 % for three bars in contact, and 33 percent for four bars in contact. (Is Code 456:200 Page-43, Cl-26.2.1.2)
Most Important Point of Lap / Maximum Manual Lapping
Lap splices shall not be used for bars larger than 36 mm; for larger diameters, bars may be welded; in cases where welding-is not practicable, lapping of bars larger than 36 mm may be permitted, in which case additional spirals.(Is Code 456:200 Page-45, Cl-26.2.5.1)
Lap Length of Column & I.M.Point
(Is Code 456:200 Page-48, Cl-26.5.3)
- The bars shall not be less than 12 mm in dia.
- The minimum number of longitudinal bars provided at a column shall be fou in rectangular columns and six in circular columns.
- The spacing of longitudinal bars measured along the periphery of the column shall not exceed 300 mm.
- Lap length for Columns – 45d.
Also, read: Difference Between Flexible Pavement and Rigid Pavement | What is Pavement | Type of Pavement
Lap length for Beams & I.M.Point
(Is Code 456:200 Page-48, Cl-26.5.2)
- The diameter of reinforcing bars shall not exceed one-eighth of the total thickness of the slab.
- The mild steel reinforcement in either direction at slabs shall not be less than 0.15 percent of the total cross-sectional area. However, this value may be reduced to 0.12 percent when high strength deformed bars or welded wire fabric are used.
- Lap length for Slabs -60d.
Lap Length for Slabs & I.M.Point
(Is Code 456:200 Page-46, Cl-26.5.1)
- Where the depth of the web at a beam exceeds 750 mm, side face reinforcement shall be provided along with the two faces.
- The total area of such reinforcement shall be not less than 0.1 percent of the web area and shall be distributed equally on two faces at a spacing not exceeding 300 mm or web thickness, whichever is less.
- The transverse reinforcement in beams shall be taken around the outer-most tension and compression bars. In T-beams and I-beams, such reinforcement shall pass around longitudinal bars located close to the outer face of the flange.
- Lap length for Beams – 60d.
Lapping Length
This amount of overlap between two bars is called “lap length”. Lapping is usually done where minimum bending stress is encountered. In general, lap length is 50d which means 50 times the bar diameter, if both bars are of same diameter.
Column Lapping
Lapping can be defined as the overlapping of two bars side by side to upto the design length. Usually, the stock length of steel bars is limited to 12m. This is for easy transportation of steel bars to the construction site. For example, imagine there is a need to build a 100ft tall column.
Lap Length
The lap length is the length provided to overlap two rebars in order to safely transfer load from one bar to another bar and alternative to this is to provide mechanical couplers. It is also known as lap splices.
Lap Length as per IS 456
For flexural tension, the lap length shall be Ld that is development length, or 30d whichever is greater is considered. Generally, development length is 41d where d is the diameter of the bar. For direct tension, the lap length should be 2 Ld or 30d whichever is greater is considered.
What Is the Minimum Lap Length?
What is the minimum lap length? For direct tension, the straight length of the lapping bar shall not be less than 15d or 20 cm. While in the case of compression lapping should not be less than 24d.
Rebar Lap Length
This amount of overlapping between two bars is called “lap length”. Lapping is usually done where minimum bending stress is encountered. In general, lap length is 50d which means 50 times the bar diameter, if both bars are of same diameter.
Minimum Lap Length for Reinforcement
This amount of overlapping between two bars is called “lap length”. Lapping is usually done where minimum bending stress is encountered. In general, lap length is 50d which means 50 times the bar diameter, if both bars are of same diameter.
Lap Distance
It is the length provided to overlap two rebars in order to safely transfer load from one bar to another bar and alternative to this is, to provide mechanical couplers.
Lap Splice Length
The lap length is the length provided to overlap two rebars in order to safely transfer load from one bar to another bar and alternative to this is to provide mechanical couplers. It is also known as lap splices.
Rebar Lapping
A lap is when two pieces of reinforcing bar (rebar) are overlapped to create a continuous line of rebar. The length of the lap varies depend on concrete strength, the rebar grade, size, and spacing. CRSI’s Reinforcement Anchorage and Splices includes tables of required lap splice lengths based on these variables.
Rebar Overlap Rule
If you touch the two bars together as they overlap, it becomes more difficult for the concrete to go in and around the rebar, and the splice is not considered as strong. So the recommended way is to bring the bars together and overlap them, but leave at least two bar diameters between the bars.
Rebar Overlap Length
This amount of overlapping between two bars is called “lap length”. Lapping is usually done where minimum bending stress is encountered. In general, lap length is 50d which means 50 times the bar diameter, if both bars are of same diameter.
Rebar Overlap
Rebar Overlap or rebar lapping occurs when a run of the rebar is longer than one solid piece. In that case, you need to overlap the rebar in that line. The length of rebar lap is usually a factor of the rebar diameter and an engineering lapping specified lapping factor. The common lapping factors are 40 and 60.
Lapping of Bars
Rebar Overlap Chart
Rebar Lap Splice Length
What Is the Lap Length?
The lap length is the length provided to overlap two rebars in order to safely transfer load from one bar to another bar and alternative to this is to provide mechanical couplers. It is also known as lap splices.
Rebar Splice Length Table
What Is Lap Splice Length?
The lap splice length is the length two rebar pieces must overlap and be tied together to create a bond as if there was no break and the run is “continuous”. So simply put, development is rebar to concrete, splice is rebar to rebar. The lengths of both splice and development do vary.
Rebar Overlap Requirements
If you touch the two bars together as they overlap, it becomes more difficult for the concrete to go in and around the rebar, and the splice is not considered as strong. So the recommended way is to bring the bars together and overlap them, but leave at least two bar diameters between the bars.
What Is Lap Length in Beam?
Lap length can be defined as the length that is provided so as to allow the overlapping of two reinforcement bars thereby ensuring safe and efficient transfer of load from one bar to another. When the reinforcement bars are placed; the length of a single reinforcement bar may not be sufficient.
What Is Lapping Length Equation?
For flexural tension, the lap length shall be Ld that is development length, or 30d whichever is greater is considered. Generally, the development length is 41d where d is the diameter of the bar. For direct tension, the lap length should be 2 Ld or 30d whichever is greater is considered.
How Far Should You Overlap Rebar?
If you touch the two bars together as they overlap, it becomes more difficult for the concrete to go in and around the rebar, and the splice is not considered as strong. So the recommended way is to bring the bars together and overlap them, but leave at least two bar diameters between the bars.
What Is the Formula for Splicing Rebar?
Lap. A lap splice is when two pieces of rebar are tied together where the bars overlap. The length of the overlap is calculated by using the equation 30 times the bar diameter. A minimum of four sets of ties are then evenly spaced along the lap length.
Why Is Lapping Used in Reinforcement?
Lap length is one of the important term in the reinforcement. During the placement of steel in Reinforced concrete structure, if the required length of single bar may fall short. To get the desired design length, lapping of two bars side by side is done. An alternative to this is to provide mechanical couplers.
How Do You Calculate Overlapping Length?
In general, lap length is 50d which means 50 times the bar diameter is provided if both bars are of same diameter. For flexural tension – Ld or 30d whichever is greater is considered. For direct tension – 2Ld or 30d whichever is greater is considered.
What Is the Best Zone of Lapping of Column?
When we provide lapping in a column, all the rebars should be lapped in zone-B as shown in the drawing. The top and bottom portion of the column, i.e. zone-A ( L/4 length ) should be avoided as there will be a maximum moment in this zone due to lateral forces acting on the column.
What Is the Lap on Rebar?
A lap is when two pieces of reinforcing bar (rebar) are overlapped to create a continuous line of rebar. The length of the lap varies depend on concrete strength, the rebar grade, size, and spacing. CRSI’s Reinforcement Anchorage and Splices includes tables of required lap splice lengths based on these variables.
What Is Staggered Lapping?
Staggered lapping means – all bars should not be lapped at same level. You can have max 50% bars which can be lap one level. Lapping should never fall in colum beam junction.
What Is Lap Zone in Column?
The top and bottom portion of the column, i.e. zone-A ( L/4 length ) should be avoided as there will be a maximum moment in this zone due to lateral forces acting on the column.
What Is the Formula of Development Length?
Generally, in practice, the development length requirement is expressed as ‘41 times Ø’ or ’41 Ø’ where 41 is the factor calculated using the above formula & Ø is the dia of the bar.
Why Development Length Is Provided in RCC?
The development length is needed to provide support to the beam to reduces the chances of the beam coming out of the concrete column. Hence it acts as a supporting member for reinforced beam in the concrete column.
What Is Development Length?
A development length can be defined as the amount of reinforcement(bar) length needed to be embedded or projected into the column to establish the desired bond strength between the concrete and steel (or any other two types of material).
What Is Effective Length?
The shortest distance between the top and bottom most points of the column at the point of bending is termed as length which effectively resists against the buckling.
What Is Bend Length?
The bend allowance is the arc length of the bend as measured along the neutral axis of the material you are using. By definition, the bend deduction is the difference between the bend allowance and twice the outside setback
What Is Lap Length in Beam?
Lap length can be defined as the length that is provided so as to allow the overlapping of two reinforcement bars thereby ensuring safe and efficient transfer of load from one bar to another. When the reinforcement bars are placed; the length of a single reinforcement bar may not be sufficient.
What Is the Lapping Length of Rebar?
Normally, lapping position is at where near the minimum shear force is acting. Normally lap length is 50D meaning 50 times the bar diameter if both bars are of same diameter. When lapping two bars of different diameters, the lap length is considered as 50 times the smaller diameter.
What Is the Standard Lap Length for Splicing Rebar?
What Is the Minimum Lapping Length of Rebar?
Normally, steel bars have a 6m length. If length of a bar is not enough to keep the reinforcement, we have to lap two steel bars. Normally, lapping position is at where near the minimum shear force is acting. Normally lap length is 50D meaning 50 times the bar diameter if both bars are of same diameter.
How Is Lap Reinforcement Calculated?
This amount of overlapping between two bars is called “lap length”. Lapping is usually done where minimum bending stress is encountered. In general, lap length is 50d which means 50 times the bar diameter, if both bars are of same diameter.
How Do You Calculate Rebar Splice Length?
How Do You Calculate Splice Length?
- Lap length in Tension
- Class A Splice: Lap Length ls = 1.0 ld.
- Class B Splice: Lap Length ls = 1.3ld.
- Lap Length for Compression Bars
- ls = 0.0005fy (d) ; [ For fy less than or equal to 60,000psi]
- ls = (0.0009fy – 24)d; [ For fy > 60,000 psi]
Is Lap Length a Code?
The Code (IS Code 456-200 Page No- 45, Cl. 26.2. 5.1c) specifies a lap length of 2Ld in situations where the member is subjected to direct tension. In no case should the lap length be less than 30Ø under flexural or direct tension and 24φ under compression.
Is Code for Lapping?
By going through this video, one can learn how to place lap in exact position in column by adhering to IS code 13920. A lap is required when two pieces of reinforcing bar (rebar) are overlapped to produce a constant line of rebar.
Why Lapping Is Provided?
A Lap is required when two pieces of reinforcing bar (rebar) are overlapped to produce a constant line of rebar. The length of the lap fluctuates according to the concrete strength, the rebar grade, size, and spacing. The objective of lap is to transmit load from one bar to another bar as well as retain continuity.
What Is Lapping in Slab?
Lap length may also be provided when the diameter of the reinforcement bar has to be changed along the length particularly during the reinforcement of columns. Such a process of overlapping the reinforcement bars side by side so as to obtain the desired design length is known as lapping.
What Is Splicing in Rebar?
A lap splice is when two pieces of rebar overlap to form a continuous reinforcement. This helps transfer loads properly throughout the structure.
What Is a Column Splice?
A column splice means the joining of two parts of a column whereas a column base transfers forces and moments at the lower end of a column to a foundation.
How Do You Make a Lap Column?
Where Do You Put Lapping in a Column?
When we provide lapping in a column, all the rebars should be lapped in zone-B as shown in the drawing. The top and bottom portion of the column, i.e. zone-A ( L/4 length ) should be avoided as there will be a maximum moment in this zone due to lateral forces acting on the column.
What Is Lapping in Reinforcement?
A lap is when two pieces of reinforcing bar (rebar) are overlapped to create a continuous line of rebar. The length of the lap varies depend on concrete strength, the rebar grade, size, and spacing. CRSI’s Reinforcement Anchorage and Splices includes tables of required lap splice lengths based on these variables.
What Is the Maximum Length of Rebar?
Reinforcing Steel Bar Length: The maximum length of any type bar shall be 60 feet. Bar lengths greater than 40 feet will require oversized vehicles for hauling.
How Many Laps Is a Column?
As per IS code 456, 30d lap length is provided in tension and minimum 24 d in compresson in column, beam and slab. But in general, 45d lap length are used for column and 60d are used for beam and RCC slab.
What Is Lap Zone in Column?
The top and bottom portion of the column, i.e. zone-A ( L/4 length ) should be avoided as there will be a maximum moment in this zone due to lateral forces acting on the column.
What Is a Splice Plate?
A splice plate is a component of the railway track. It is a piece of metal bolted onto the rails, making it possible to connect two rails in a row. Splice plates are often used near switches or other sensitive areas. Elsewhere on the track the joint between two rails is generally welded.
What Is the Minimum Splice Length for Rebar?
Joint reinforcement must have a minimum splice length of 6 in. (152 mm) to transfer shrinkage stresses.
How Long Is a Length of Rebar?
Reinforcing bars (rebars) come in lengths of up to 60 feet.
Is Code a Lap Zone?
Lap Zone In Column As Per IS Code | Column Reinforcement Lapping. When two pieces of rebar are overlapping, a lap is needed to make a constant reinforced line of rebar. The lap length varies depending on the strength of the concrete, the grade of rebar, and size and spacing.
How Much Do You Overlap Rebar?
If you touch the two bars together as they overlap, it becomes more difficult for the concrete to go in and around the rebar, and the splice is not considered as strong. So the recommended way is to bring the bars together and overlap them, but leave at least two bar diameters between the bars.
How Do You Determine Lap Length in Steel Reinforcement?
So the second bar is kept closely to the first bar and overlapping is done. This amount of overlapping between two bars is called “lap length”. Lapping is usually done where minimum bending stress is encountered. In general, lap length is 50d which means 50 times the bar diameter, if both bars are of same diameter.
What Is the Difference Between Lap Length and Development Length?
Lap length is to be provided to safely transfer the load. Development length is provided to transfer the load from steel to concrete. It is also known as anchorage length.
Is Code for Overlapping?
As stated by IS Code 456-2000, overlapping should not remain under 75 mm. Overlapping means the extra length arranged in the reinforcement steel bars. Here, two lengths are overlapped and attached with a wire to increase the length of any steel bar whenever necessary.
What Is Anchorage Length in Reinforcement?
Meaning of anchorage length is the length required for development of stress in the rebars, this is obtained by providing the required development length or hook/bends if sufficient length cannot be achieved.
What Is the Lap Length for 12mm Bar?
Lap length for 12mm bar used in beam:- assuming 12mm bar of Fe500 provided in RCC roof slab, their lap length should be 60d, where d is diameter of rebar which are going to be used, calculation of lap length for 12mm bar = 60×12= 720mm (0.72m) or 2.36feet, so lap length for 12mm bar used in beam is 720mm (0.72m) or 2.36feet.
What Is Lap Length of Column?
The lap length is the length provided to overlap two rebars in order to safely transfer load from one bar to another bar and alternative to this is to provide mechanical couplers. It is also known as lap splices.
What Is Lapping in Rebar?
A lap is when two pieces of reinforcing bar (rebar) are overlapped to create a continuous line of rebar. The length of the lap varies depend on concrete strength, the rebar grade, size, and spacing. CRSI’s Reinforcement Anchorage and Splices includes tables of required lap splice lengths based on these variables.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Difference Between One Way Slab and Two Way Slab | What is Slab
- What is Rate Analysis | Rate Analysis of Earth Work, Brick, Concrete and Plaster
- Mortar Vs Grout | What Is Motor and Grout | Type of Motor and Grout | Difference Between Mortar and Grout
- Detail of Beam Connection | Simple Framing Connection | Semi-Rigid Framing Connection | Rigid Frame Connection
- What Is Structural Settlement | Causes For Structural Settlement | What Is Soil Settlement & Foundation Structural Settlement
Originally posted 2023-05-10 02:00:10.


Leave a Reply