What Is Shotcrete?
Important Point
Shotcrete is a kind of refined concrete drizzled by gas hose-pipe nozzle at high pressure & velocity on a projectile motion on a prepared wall surface. It is strengthened by conventional steel rods, steel mesh or fibres.
It is often utilised in tunnels, underground walls, retaining walls, drainage systems & swimming pools for interim support. For slope protection with wire mesh and in some confined areas wherever prosaic concreting cannot be done.
It can be sprayed on any type of surface (vertical or overhead). The shotcrete method needs less formwork and is more economical and cheap (needs only a small industry to get manufactured). It forms a good chemical bonding among a variety of materials.
Shotcrete & Concrete
Concrete is a building material that comes with an exceeding diversity of choices, together with lightweight, heavyweight, porous, and fibre-reinforced, to suit a range of construction needs. It consists of refined rock-dust & water paste that solidifies.
Shotcrete is a specific style of concrete that can either be dry-mix or wet-mix. It has become acclaimed for its unique application technique that is distinctive from prosaic concrete.
How Does the Application of Shotcrete Dissent from Concrete?
The main distinction between shotcrete and concrete happens during its placement. Concrete is applied by employing a mixing truck, which prepares the mixture and pours it onto the ground.
The fresh concrete is then sprayed. Conversely, shotcrete is placed using a cement gun. The gun applies the mixture at a high rate, which gives the end product high strength, high sturdiness, and low permeability.
Shotcrete Technology
Ingredients:
- Cement.
- Sand (Natural/ Crushed).
- Coarse Mixture (Below 10mm).
- Admixture.
- Water.
- Fly ash/ Microsilica.
Types of Shotcrete Technology
There are two types of Shotcrete Technology. Which is as follows.
- Dry-Mix Shotcrete.
- Wet-Mix Shotcrete.
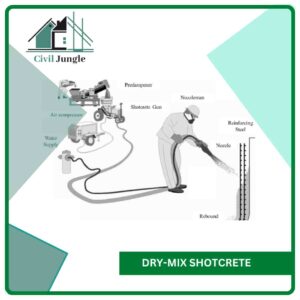
#1. Dry-Mix Shotcrete-
It involves inserting the dry ingredients into a gun and then spray them through a hose to the nozzle. The inner part of the nozzle possesses a water ring which uniformly injects water into the mixture as it is being oozed out from the nozzle and propelled on the wall surface.
The water and the dry mixture are not thoroughly mixed but is completed as the mixture hits the receiving surface. This requires a skilled nozzleman, peculiarly in heavily bolstered sections.
Advantages of Dry-Mix Shotcrete
- The dry mix process is beneficial in repair applications when it is necessary to stop & adjust frequently.
Disadvantages of Dry-Mix Shotcrete
- Dust will be higher as we are using the dry ingredients. It is not applicable where the shotcrete quantity is applied more frequently.
#2. Wet-Mix Shotcrete
In wet-mix shotcrete, ready-mix concrete is used, which is sprayed through delivery paraphernalia such as a concrete pump which propels the mixture through the delivery hose where compressed air and accelerator is added at the nozzle point.
Advantages of Wet-Mix Shotcrete
- Less rebound (shotcrete falls down due to paucity in setting).
- Less dust compared to dry-mix shotcrete.
- Larger volume can be placed in lesser time.
Disadvantages of Wet-Mix Shotcrete
- A highly skilled operator is needed in spraying.
- W/c, pressure and accelerator dosage has to be unambiguous.
Also, Read: Fish Ladder | What Is Fish Ladder | Types of Fish Ladder | Fish Ladders in Dams
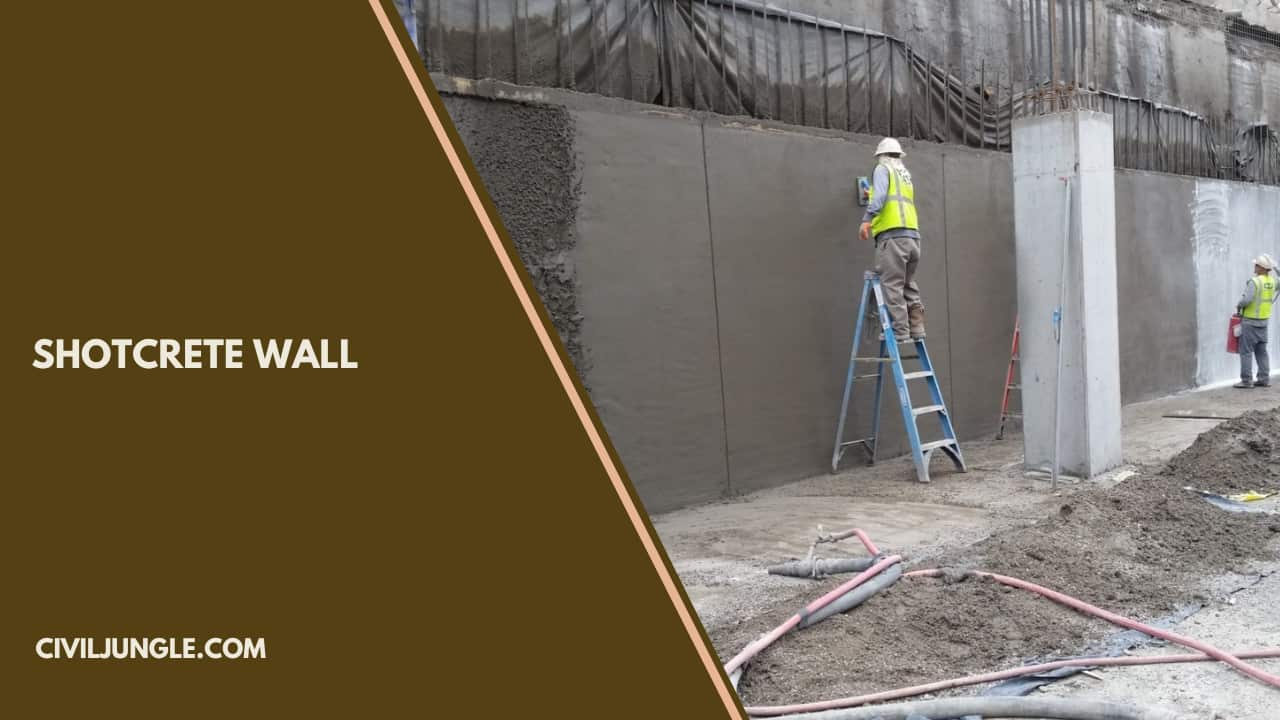
Shotcrete Wall
Shotcrete wall placement gives the subsequent benefits for quicker installation:
-
- Set concrete wall thickness and vertical alignment.
- Shotcrete wall at a faster rate than form-and-pour.
-
- Finish concrete to any specification.
Also, Read: Types of Pitched Roofs
Shotcrete Wall Benefits:
Shotcrete Wall Benefits are as follows.
- Potentiality to place walls top-down, bottom-up or a full excavation.
- Substantially increase production compared to cast in situ concrete walls.
- ACI shotcrete specifications are readily available.
- Effortlessly incorporate shotcrete as an amendment order during construction.
- High strength, low permeability and high durability.
- Faster concrete set-up reduces labour costs.
- Better bonding to the receiving surface.
- Reduction of forming materials by up to 100%.
- No extra concrete footings required for wall supports.
- Diminished crane time for form setting and concrete pouring.
Properties of Shotcrete:
Properties of shotcrete are as follows.
- A small maximum size mixture used and cement content is high.
- It is ought to enhance sturdiness in most cases.
- Whereas typical concrete is consolidated by vibration, shotcrete is consolidated by the impact of a high-velocity jet bashing on the surface.
- This method not only increases the cement content due to rebound but also brings about completely dissimilar air-void systems affecting the sturdiness of shotcrete.
- The application procedures have a greater effect on the in-place properties of shotcrete than the mix proportions.
- Shotcrete specimens usually sawed from test panels of about one-meter square and 75 millimetres dense made by gunning out plywood.
Applications of Shotcrete:
Applications of shotcrete are as follows.
- Shotcrete is widely employed in different construction such as skinny overhead vertical or horizontal surface, notably the curved or folded sections, canal, buildings, marine structures, bridges, reservoir, and tunnel lining.
- It is additionally employed in tunnels, canals, reservoirs, swimming pools, water retaining structures, and pre-stressed tanks.
- Shotcrete has successfully been utilised in the stabilisation of rock slopes, underground excavations and temporary protection of freshly excavated rock surfaces.
- It may be a utility for protection against long-term corrosion of pilling, coal bunker, oil tanks, steel building frames, and other structures, renovation of old buildings and fire vandalised structures as well as in encasing steel to form the structure water-resistant.
- These are developed for high-temperature applications, like the refractory lining of kilns, chimneys, furnaces, etc.
- They are also used for waterproofing walls.
Also, Read: What Is Guniting | Set Guniting Systems | Advantage | Disadvantage
Advantages of Shotcrete:
The advantages of shotcrete are as follows.
- The shotcrete can be applied by a nozzle from a secured haughtiness. It requires no vibration or compaction after placement since it is blown into place under pressure.
- More economical than prosaic concrete and requires less formwork. It is a reasonable thanks to build concrete in curves and serpentine shapes that are arduous or unfeasible with traditional concrete forming, such as those required in tanks, domes, swimming pools, and skate parks.
- Eximious bonding in nature which makes the concrete layers terribly robust.
- Among the benefits, it does not need a tortuous system of forms just like the more amicable poured-in-place concrete, since it is applied as a stiff paste and is solely a one-sided type, or none the last bit if it is applied over compacted soil.
- It can be used with steel reinforcing bars, welded wire reinforcing mesh, fibre reinforcement mixed with the concrete, or with no reinforcement.
- It has identical non-combustible and fire-resistant qualities as concrete that has been formed and poured in a prosaic manner.
- It minimises man-power.
- Helps to manage cement-water ratio.
Also, Read: Concrete Mix Ratio | What Is Concrete Mix Ratio | Types of Concrete Mix Ratio
Disadvantages of Shotcrete.
The Disadvantages of shotcrete are as follows.
- The primary pitfall of shotcrete compared to slooshed concrete is the bulk of your time that it takes when utilised for Brobdingnagian foundations, structural piers, and other structures with giant cross-sections, in juxtaposition to using prosaic forms for these giant structures.
- Another disadvantage is the dusting drawback.
- Two common issues when applying shotcrete are gravel within the concrete concoction that is too colossal, which hinders with the spraying of the concrete; and ready-mixed concrete that is too wet so that it does not adhere well to vertical and overhead surfaces.
- Production cost is incredibly high.
- Much concrete is squandered in comparison to prosaic concrete.
- High skilled manpower needed to perform the work.
- The procedure is sophisticated to some extent.
Also, Read: What Is Water Cement Ratio | Water-Cement Ratio and Concrete Strength | Role of Water in Concrete
Shotcrete
Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete projected at high velocity primarily on to a vertical or overhead surface. The shotcrete process requires less formwork and can be more economical than conventionally placed concrete. Shotcrete is applied using a wet- or dry-mix process.
What Is Shotcrete?
Shotcrete, gunite, or sprayed concrete is concrete or mortar conveyed through a hose and pneumatically projected at high velocity onto a surface, as a construction technique, first used in 1914. It is typically reinforced by conventional steel rods, steel mesh, or fibers.
Shotcrete Concrete
A. Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete projected at high velocity primarily onto a vertical or overhead surface. The shotcrete process requires less formwork and can be more economical than conventionally placed concrete. Shotcrete is applied using a wet- or dry-mix process.
Shotcrete Technology
Advancements In Shotcrete Technology. Shotcrete is a cement-based mixture pneumatically projected at high velocity onto a receiving surface. These novel shotcrete materials are produced through the addition of new generations of chemical admixtures, supplementary cementitious materials and reinforcement fibres.
Advantages of Shotcrete
The use of shotcrete–sprayed concrete in construction activities makes the structure less porous which increases the bond strength and also helps in lowering the construction time and reduces costs as well.
Disadvantages of Shotcrete
The primary disadvantage of shotcrete compared to poured concrete is the amount of time that it takes when used for large foundations, structural piers, and other structures with large cross-sections, compared to using conventional forms for these large structures.
Application of Shotcrete
In building repairs, shotcrete is commonly used for repair of fire and earthquake damage and deterioration, strengthening walls, and encasing structural steel for fireproofing. The repair of structural members such as beams, columns, and connections is common for structures damaged by an earthquake.
Uses of Shotcrete
In building repairs, shotcrete is commonly used for repair of fire and earthquake damage and deterioration, strengthening walls, and encasing structural steel for fireproofing. The repair of structural members such as beams, columns, and connections is common for structures damaged by an earthquake.
What Is Shotcreting?
Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete projected at high velocity primarily on to a vertical or overhead surface. The wet-mix shotcrete process mixes all ingredients, including water, before introduction into the delivery hose. The dry-mix shotcrete process adds water to the mix at the nozzle.
How Strong Is Shotcrete?
The compressive strength of shotcrete is 25 ~ 40 MPa, the tensile strength is 2.0 ~ 2.5 MPa, and its bonding power with stone is 1.0 ~ 1.5 MPa, which can meet the requirements of underground structures completely.
Shotcrete Cost
It is also known as free-form concrete, is highly versatile, and produces some of the strongest and most watertight in-ground pools. The cost for a shotcrete pool is from $55 to $60 per square foot.
What Do You Need for Shotcrete?
A vast range of equipment can be used to place shotcrete, including gunning machines, pre-dampeners, dosing pumps, pumps, combination mixer pumps, mixers, and nozzle carriers. Some equipment is used for wet process and some for dry process.
Is Shotcrete Better Than Gunite?
It takes less time to apply shotcrete than gunite. Because there are less rebound materials formed, you reduce the risk of weak spots. Shotcrete is pre-mixed, allowing it to form a consistent and strong coating.
Is Shotcrete Stronger Than Concrete?
Frequently used in underground applications, shotcrete is a wet- or dry-mix concrete that is pneumatically propelled at high velocity through a hose and nozzle. And because the spray application process reduces the water/cement ratio, it’s generally stronger than CIP.
Is Shotcrete Stronger Than Gunite?
With Shotcrete, There is no rebound, so this problem simply cannot occur. Shotcrete also happens to be substantially harder than Gunite. Shotcrete is hard as a rock. That’s why at Bluewater pools, we prefer Shotcrete over gunite for our pools.
What Is Application of Shotcrete How It Is Done?
Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete projected at high velocity primarily on to a vertical or overhead surface. The dry-mix shotcrete process adds water to the mix at the nozzle. Shotcrete is used in new construction and repairs and is suitable for curved and thin elements (ACI 506R).
Which Is More Expensive Gunite or Shotcrete?
Gunite tends to be less expensive than shotcrete, and it can result in fewer errors in the construction process.
What Is the Compressive Strength of Shotcrete?
Shotcrete having a specified compressive strength of 4000 psi (28 MPa) or greater is considered structural shotcrete. Shot- creting can be applied by one of two processes: wet-mix or dry-mix. Shotcrete is further described according to the size of aggregate used (coarse or fine).
How Much Does Shotcrete Cost?
The cost for a shotcrete pool is from $55 to $60 per square foot.
How Thick Can Shotcrete Be Applied?
There is no stated maximum thickness for shotcrete used in shear walls or any other type of wall. Walls have been successfully placed to a thickness of 36 in. (914 mm) for some time. The two main concerns are the heat of hydration and proper encapsulation of the reinforcing steel.
Is Shotcrete More Expensive Than Gunite?
Gunite generally allows builders to take more time to complete the project properly, since they can stop and start as needed. Gunite tends to be less expensive than shotcrete, and it can result in fewer errors in the construction process.
How Long Does Shotcrete Need to Cure?
Shotconcrete, when applied using the shotcrete process, or cast-in-place, needs to cure for 7 days. Water is the best curing method (7 continuous days)
How Many Types of Shotcrete Are There?
The two types of shotcrete processes, dry shotcrete (also known as gunite), and wet shotcrete, have grown steadily in popularity in both concrete repair and new construction. This article will compare and contrast the two shotcrete processes.
What Is the Difference Between Shotcrete and Concrete?
Concrete pools can be made of either shotcrete or gunite. The difference is when the concrete mixes with the water. Shotcrete refers to wet concrete that’s already fully mixed before it’s shot out of a hose. Gunite is dry concrete mix that only mixes with water at the nozzle when it’s sprayed.
What Is the Difference Between Gunite and Shotcrete?
We use the term gunite to mean a dry concrete mix, and we call it shotcrete when dealing with wet concrete. With shotcrete, the concrete is already mixed in a cement truck before you shoot it out of a hose, while gunite is a dry mix that combines with water at the nozzle when you spray it.
Why Is Shotcrete Used?
Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete projected at high velocity primarily on to a vertical or overhead surface. The dry-mix shotcrete process adds water to the mix at the nozzle. Shotcrete is used in new construction and repairs and is suitable for curved and thin elements (ACI 506R).
Where Is Shotcrete Used?
Because it can take any shape, is easily coloured, and can be sculptured after application, shotcrete is used for a variety of fancy concrete structures, including artificial rock walls, zoo enclosures, canopy roofs, refractory linings, pools, and dams.
What Is the Shotcrete Concrete?
Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete projected at high velocity primarily on to a vertical or overhead surface. The impact created by the application consolidates the concrete. Shotcrete is applied using a wet- or dry-mix process.
What Is the Purpose of Shotcrete?
Shotcrete is used to reinforce both temporary and permanent excavations. It may be employed, in concert with lagging and other forms of earth anchor, to stabilize an excavation for an underground parking structure or hi-rise during construction.
How Shotcrete Is Done?
Wet-mix shotcrete involves pumping of a previously prepared concrete, typically ready-mixed concrete, to the nozzle. Compressed air is introduced at the nozzle to impel the mixture onto the receiving surface.
What Are the Advantages of Using Shotcrete in Repair?
- Excellent bonding in nature makes the concrete layers very strong.
- It is more economical than conventional concrete and requires less formwork.
- The Concrete can be applied by a nozzle from a safe distance.
Types of Shotcrete
The two main types of shotcrete are dry-mix shotcrete (gunite) and wet-mix shotcrete. Dry-mix shotcrete involves adding water at the nozzle, while wet-mix shotcrete is pre-mixed with water before being sprayed. Shotcrete can also be classified based on its purpose, such as structural shotcrete, repair shotcrete, pool shotcrete, or artistic shotcrete.
Shotcrete Process
Shotcrete is applied using a wet- or dry-mix process. The wet-mix shotcrete process mixes all ingredients, including water, before introduction into the delivery hose. The dry-mix shotcrete process adds water to the mix at the nozzle.
Shotcrete Construction
Shotcrete is a mixture of aggregate and portland cement, conveyed by compressed air to the nozzle of a spray gun, where water is added. The wet mixture is then sprayed in place and may be carved or troweled almost immediately.
Shotcrete Concrete Mix Ratio
The ratio of cement to aggregate should be different according to the construction process. When dry spraying is adopted, the weight ratio of cement to sand and stone should be 1:4 -1:4.5. When wet spraying is applied, the weight ratio of cement to sand and stone should be 1:3.5~1:4.0.
How Does Shotcrete Work?
Shotcrete is a mortar or high performance concrete conveyed through a hose and pneumatically projected at high velocity onto a backing surface. It is the force of this spraying action that leads to compaction of the concrete or mortar which then forms layers of concrete to the required thickness .
Shotcrete Vs Concrete
For waterproofing performance, conventional CIP concrete is more reliable than shotcrete, and has proven so through decades of successful installations. Shotcrete is popular because it’s less expensive to install. However, its use has resulted in higher incidences of water ingress in below-grade foundations.
Shotcrete Uses
Shotcrete is used to reinforce both temporary and permanent excavations. It may be employed, in concert with lagging and other forms of earth anchor, to stabilize an excavation for an underground parking structure or hi-rise buildings during construction.
Like this post? Share it with your friends!
Suggested Read –
- Types of Tunnels
- Types of Tile Roofs
- Concrete Wall Finish
- Difference Between Marble and Granite | What Is Marble and How Is It Made | What Is Granite and How Is It Made
- What Are Walls | What Is Interior Walls | Types of Interior Wall Materials | Types of Wall Construction | Types of Load Bearing Wall
- Building Layout | How to Building Layout | What Is Method of Layout of Building | Control Lines of Construction | Construction Layout
- Emulsion Paint Vs Oil Based Paint | Purpose of Providing Paints | Properties of Good Paint | Properties of Good Paint | What Is Oil Based Paint
- Difference Between Sketching and Drawing | What Are Conceptual Sketches | Architecture Concept Drawing | Types of Drawings for Building Design
- Definition of Shear Force and Bending Moment | What Is Shear Force | What Is Bending Moment | Relation Between Loading, Shear Force & Bending Moment
Originally posted 2023-07-06 15:01:53.














Leave a Reply